Magnetic properties classify minerals based on specific magnetic susceptibility. During magnetic separation, the greater the difference in specific magnetic susceptibility of minerals, the easier the separation.
Magnetic classification of minerals
According to magnetism
Magnetism can be seen as the result of the motion of charged particles within matter and is one of the fundamental properties of matter. All kinds of substances in nature have different degrees of magnetism; most have very weak magnetism, and only a few have strong magnetism. In terms of magnetism, matter can be divided into three categories:
- Paramagnetic substance
- Diamagnetic substance
- Ferromagnetic substances (ferrimagnetic, antiferromagnetic)
According to the size of mineral-specific magnetic susceptibility
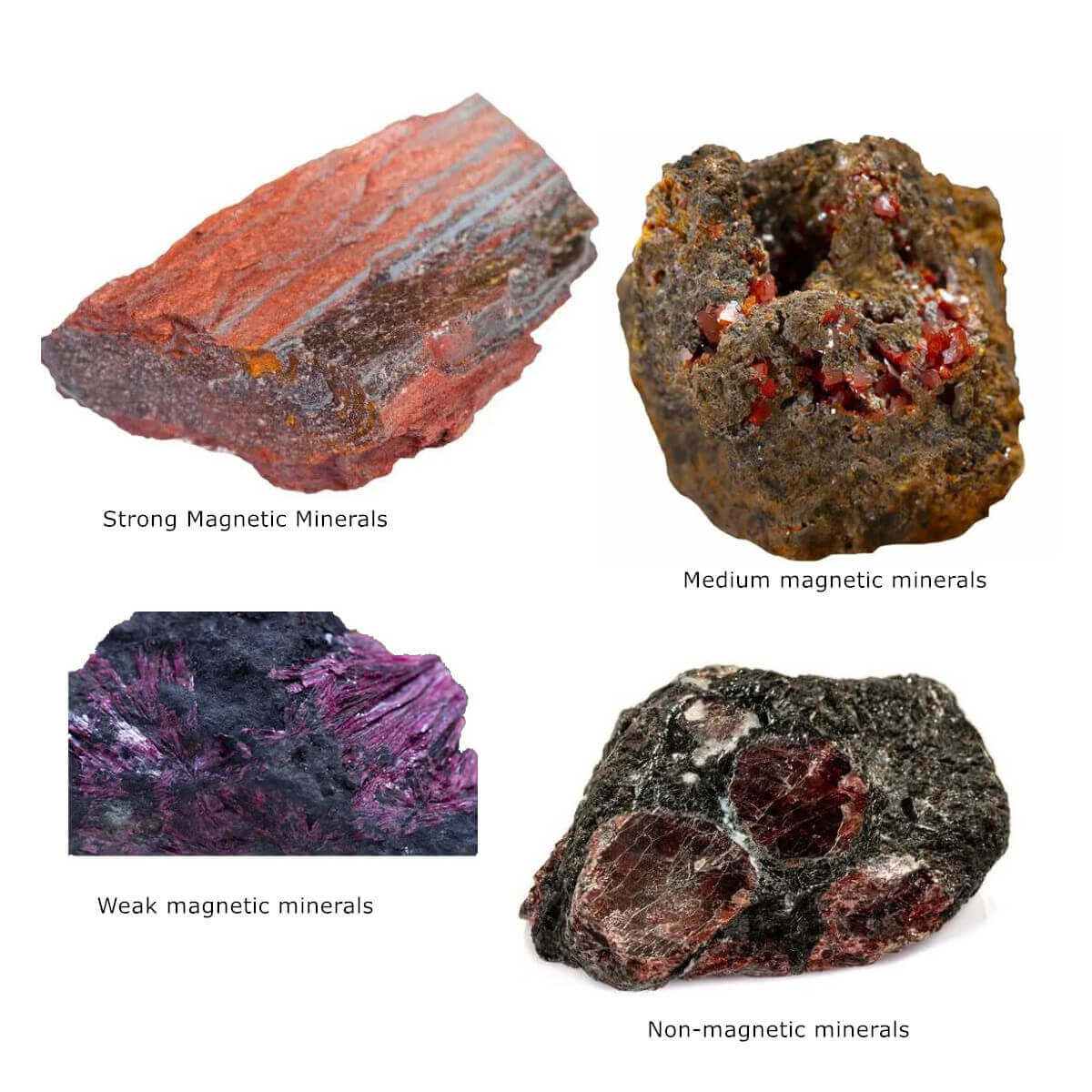
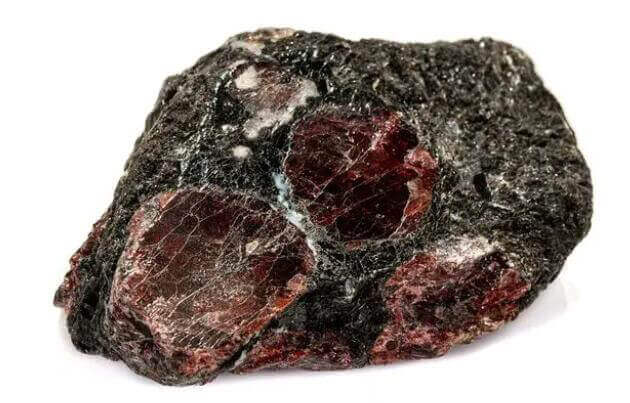
1. Strong Magnetic Minerals
Its specific magnetic susceptibility X is greater than 3000×10-6 cubic centimeters/gram. It can be selected in a weak magnetic separator with a magnetic field strength H = 7200~136000 A/m, and it is an easy-to-select mineral. There are very few minerals belonging to this category. Mainly include magnetite, maghemite (gamma hematite), titanium magnetite, pyrrhotite, zinc iron spinel, etc. Most of these minerals are ferrimagnetic.
Magnetic characteristics of strong magnetic minerals
Magnetite can be used as a representative of strong magnetic minerals, which is ferrimagnetic; because of the internal magnetic domain structure (that is, a small area of spontaneous magnetization), its magnetic properties are relatively complicated, and its magnetic characteristics are summarized as follows:
①The magnetization intensity and the magnetization coefficient value are very large, there is a magnetic saturation phenomenon, and the magnetic saturation can be achieved under the action of a low external magnetic field intensity;
② There is a curvilinear relationship between the magnetization intensity, the magnetic susceptibility coefficient, and the external magnetic field strength, and the magnetic susceptibility coefficient is not a constant. In addition to being related to mineral properties, magnetization is also related to the change of the external magnetic field;
③ Magnetite has a hysteresis phenomenon. When it leaves the magnetization field, it retains a certain amount of remanence; Adding a reverse magnetic field to remove the remanence is necessary. The diamagnetic field strength Hc that completely removes the residual magnetism is called the coercive force
④ Its magnetic change is related to temperature. When the temperature is higher than the critical value—the Curie point, the internal magnetic domain structure disappears, showing paramagnetism;
⑤ Its magnetic crossing is not only related to the strength of the external magnetizing field but also affected by the cobalt’s shape, particle size, and oxidation degree.
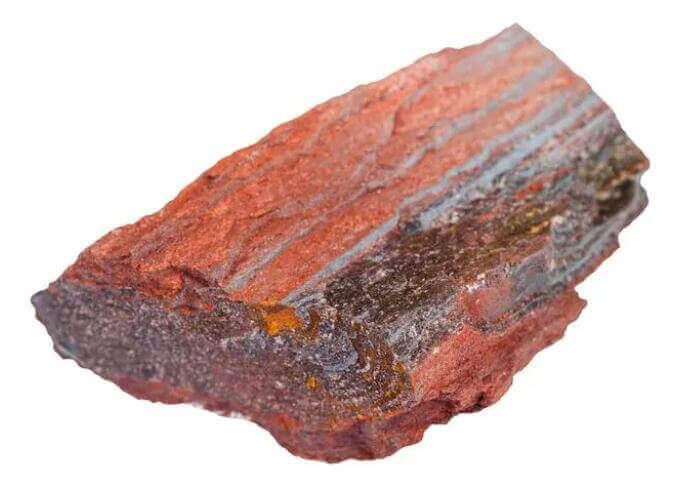
2. Medium magnetic minerals
Its specific magnetic susceptibility X is between (600~3000)x10-6 cubic centimeters/gram. The only minerals belonging to this category are ilmenite and pseudo hematite. A magnetic separator with a magnetic field strength H of 160,000~480,000 A/m is required to select such minerals.
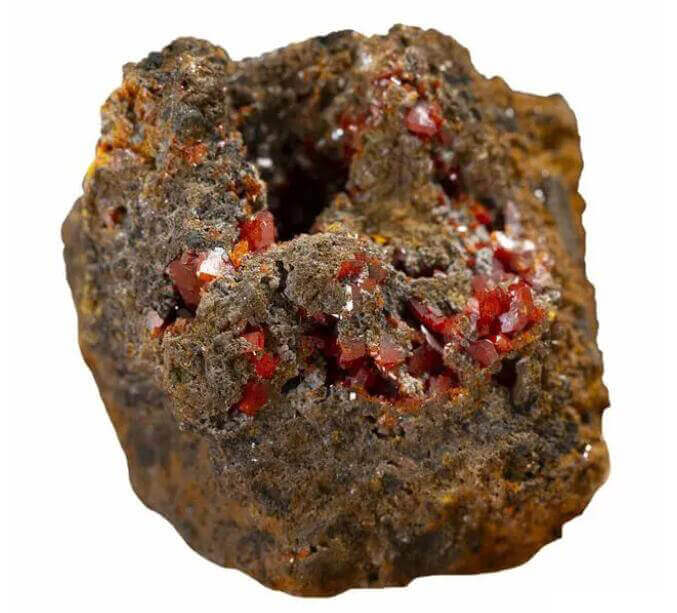
3. Weak magnetic minerals
Its material-specific magnetic susceptibility X is between (15~600)x10-6 cubic centimeters/gram. It can be selected in a strong magnetic separator with a magnetic field strength of H=480000~1600000A/m. Many minerals belong to this category, some of which are easy to choose, and some are difficult to choose. Mainly include most iron and manganese minerals – hematite, specularite, limonite, siderite, manganese ore, pyrolusite, manganese ore, rhodochrosite, etc.; some minerals containing chromium and tungsten – ferrochrome ore, wolframite, etc.; some rock-forming minerals – biotite, hornblende, epidote, chlorite, serpentine, olivine, garnet, pyroxene, etc. The large ones of these minerals are paramagnetic, and some are antiferromagnetic.
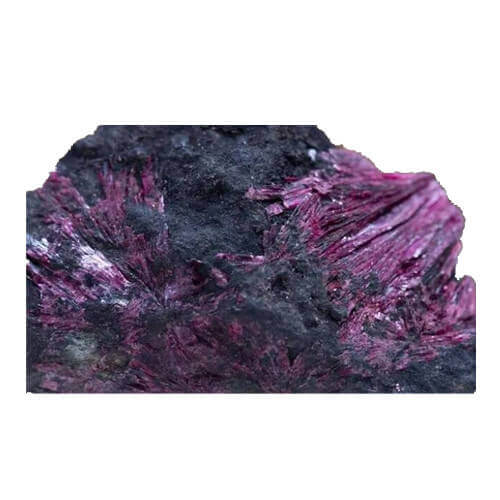
4. Non-magnetic minerals
Its specific magnetic susceptibility coefficient is less than 15×10-6 cubic centimeters/gram. There are many minerals belonging to this category. Mainly include some metal minerals – chalcocite, galena, sphalerite, stibnite, scheelite, cassiterite, gold, etc. Most non-metallic minerals – sulfur, coal, graphite, diamond, gypsum, kaolin, etc.; most rock-forming minerals – quartz, feldspar, calcite, etc. Some of these minerals are paramagnetic, and some are diamagnetic. The so-called non-magnetic minerals are not without magnetism but are extremely small.
The above classification is a rough classification under modern technical conditions because many factors affect the magnetic properties of minerals. Even the same minerals are not identical in their magnetic properties.
Generally speaking, the choice of magnetic separator is as follows: strong magnetic separators select weak magnetic minerals, and weak magnetic separators select weak magnetic minerals. With the development of magnetic separation technology, the boundary between weak magnetic minerals and non-magnetic minerals will change. The lower limit of the specific magnetic susceptibility of weakly magnetic minerals is constantly decreasing, an inevitable trend in the development of magnetic separation and magnetic separators.
JXSC Machine is a renowned and reputable company providing mineral solutions and manufacturing mining equipment. It specializes in designing and manufacturing various magnetic separators for applications and mining scenarios. JXSC offers an extensive portfolio of magnetic separation equipment, tailored to meet the diverse needs of their clients.
Some of the popular products include:
- Magnetic Drum Separator: These separators use a rotating drum to capture and separate magnetic particles from the ore mixture. They are effective in removing tramp iron and other ferromagnetic contaminants.
- Magnetic Pulley: Utilized for continuous extraction of ferrous metals from conveyed material on conveyor belts, magnetic pulleys are essential in recycling and bulk handling industries.
- Overband Magnetic Separator: Designed to attract and remove unwanted tramp ferrous metal from conveyed material, overband separators are crucial in ensuring the smooth functioning of downstream equipment.
- Magnetic Grill/Grid: These separators consist of a series of magnetic tubes arranged in a grid, effectively separating fine ferrous particles from free-flowing materials.
- Magnetic Separator Machine: JXSC manufactures custom magnetic separator machines tailored to specific project requirements and mineral compositions.
Magnetic Separators Features
- Enhanced Mineral Recovery: JXSC’s magnetic separators help improve mineral yield and recovery rates, leading to higher profitability for mining operations.
- Efficient Removal of Contaminants: By eliminating undesirable ferrous particles, the equipment ensures the purity and quality of the final mineral products.
- Reliable Performance: JXSC’s products are known for their robustness, reliability, and ease of maintenance, ensuring minimal downtime and increased productivity.
As a professional mineral solution and mining equipment manufacturer, JXSC’s expertise in Magnetic Separation is vital in optimizing mining processes, enhancing efficiency, and contributing to the success of mining projects worldwide. Their commitment to innovation and customer satisfaction makes them a preferred choice for companies in the mining industry seeking high-quality and reliable magnetic separation solutions.
LATEST PRODUCTS
Heavy Plate Feeder
Capacity: 100-240 m3/h Power: 15-45 kW Speed: 0…
Plate Magnetic Separator
【Capacity】8-35 t/h 【Power】1.5-3 kW 【Applic…
Slurry Magnetic Separator
【Capacity】10-100 m3/h 【Feeding Material Densi…