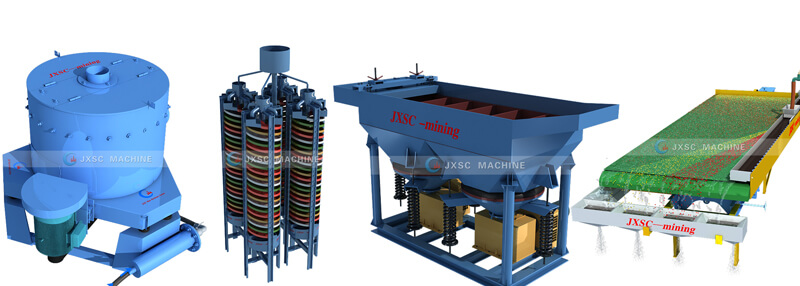
Since the cyanidation process was applied to mines for gold and silver in 1887, it has a history of nearly one hundred years and the process is relatively mature. Due to its high recovery rate and strong adaptability to the ore, it is still one of the main ways of gold production.
The cyanidation process can be divided into agitating cyanidation and diafiltration cyanidation. Stirring cyanide for the treatment of gravity separated, mercury-contained tailings and flotation gold-bearing concentrates, or for total mud cyanidation. Diafiltration cyanidation for the treatment of flotation tailings and low-grade gold-bearing ores heap leaching.
The conventional cyanidation process is a very mature process, which includes preparation of leaching raw materials; stirring cyanide leaching; countercurrent washing solid-liquid separation; leaching liquid purification and deoxidation; zinc powder replacement and pickling; and smelting ingots.
a. Preparation of leaching raw materials: crush and grind the mine ore, prepare a slurry suitable for cyanide leaching. Grinding fineness depends on the embedding characteristics of natural gold. For gold-bearing quartz vein ore, it is generally ground to 60-70%-200 mesh; while for sulfide mineral-bearing gold ore, it is mostly flotation and enrichment, and the concentrate is reground to 90-95%-325 mesh; for the ore with high content of arsenic or high pyrrhotite, it is subjected to flotation concentrate roasting, desulfurization and arsenic removal, and calcination is carried out for cyanidation; in addition, there are ores containing high carbon and interfering with cyanide leaching.
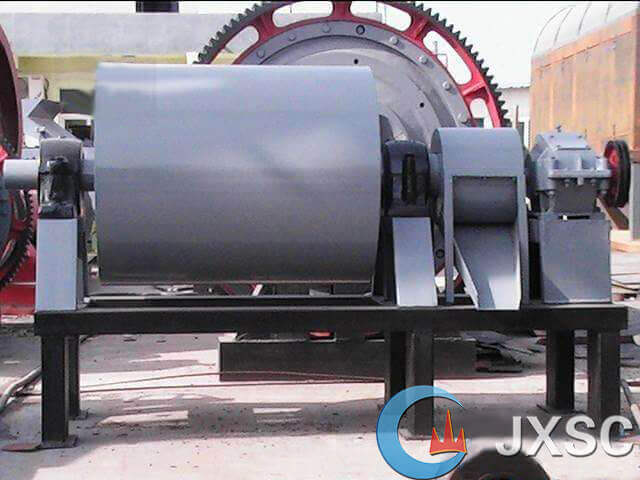
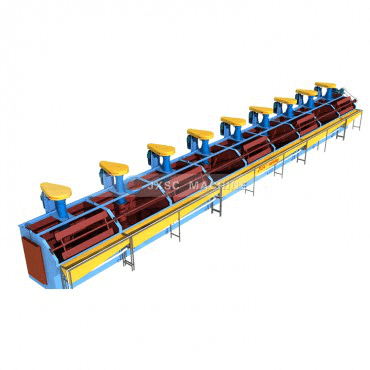
b. Stirring cyanide leaching: under conditions of a slurry concentration of 35 to 50%, a pH of 10 to 10.5, and a cyanide concentration of 0.03 to 0.06%, the mixture is fully agitated and leached for more than 24 hours. More than 95% of the gold is dissolved as a gold cyanide complex.
The mixing and immersion tank has two types: mechanical stirring type and air stirring type.
c. Countercurrent washing solid-liquid separation: In order to fully separate the cyanide leachate from the gold residue, a plurality of thickeners are generally used to form a multi-stage countercurrent washing.
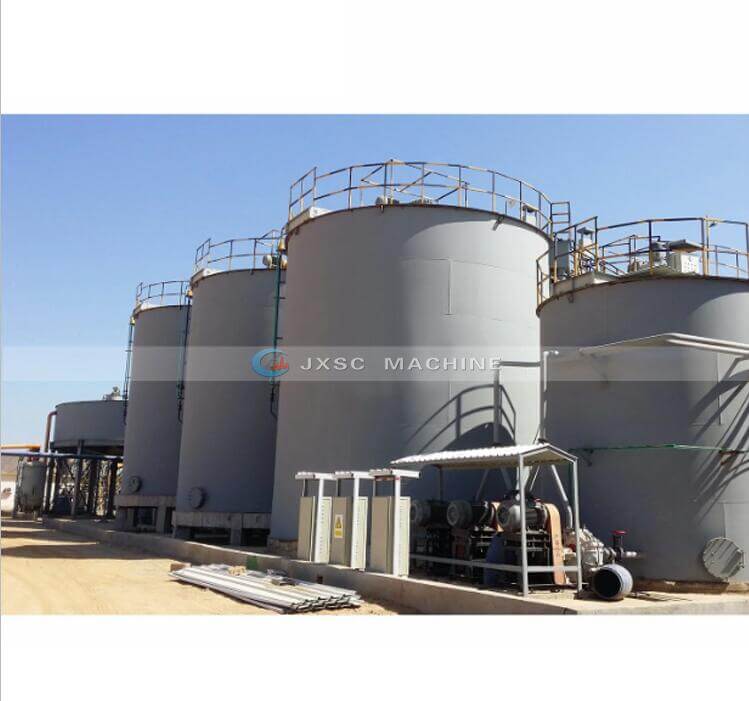
d. Purification and Deoxidation of Leachate: The leachate (Pregnant solution) obtained from the washing operation usually contains 70 to 80 ppm or more of a solid suspension. In order to prepare conditions for the zinc powder replacement operation, it is necessary to reduce the suspended matter content in the noble liquid to 5 to 7 ppm and the oxygen content to 1 ppm, so the noble liquid should be purified and deoxidized.
e, zinc powder replacement and pickling: replacing the gold cyanide complex in the solution with zinc powder to precipitate gold. In order to obtain a more efficient displacement reaction of the zinc powder, a lead salt of about 0.005% and a cyanide concentration of about 0.05% should be maintained in the solution.
f, smelting ingot: gold mud and flux generally according to 1:0.8 ~ 1, the ratio of borax 30 ~ 40%, saltpeter 25%, quartz sand 15 ~ 20%, fluorite 5 ~ 10%, the other is soda, oxidation Manganese, etc. The slag is smelted at a furnace temperature of 1000 to 1100 ° C for about 3 hours to obtain a gold ingot (composite gold) containing 85% or more of gold and silver.