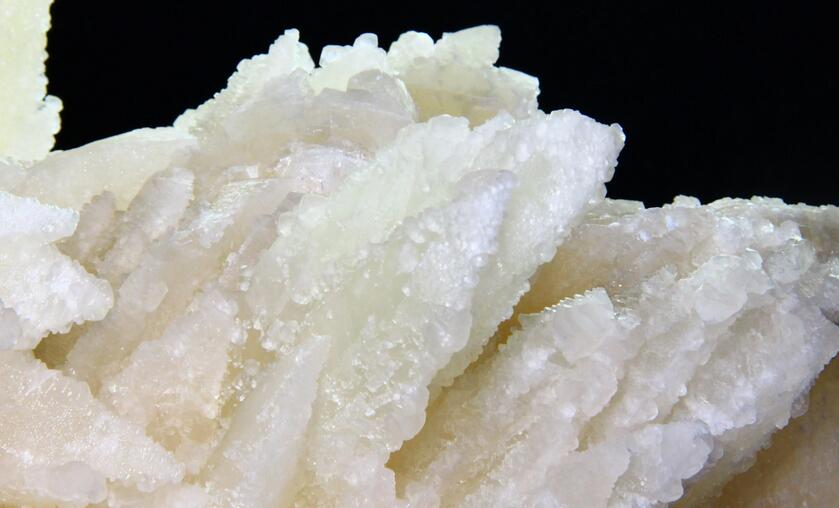
Magnesite Introduction
Magnesite was originally used as a refractory material, and it is still one of the essential refractory auxiliary materials for the smelting industry. With the development of science and technology, its use is becoming wider and wider, and its demand is also increasing. It has become an indispensable mineral raw material for the national economy. As far as magnesite is concerned, China is not only a large resource country but also a large producer. Two-thirds of the world’s magnesite reserves are concentrated in China, and one-half of the output is provided by China. In the world magnesite market, China has a pivotal position. Magnesite is magnesium carbonate. Its chemical formula is magnesium carbonate (MgCO3). The theoretical composition is MgO47.81% and CO252.19%. The density is 2.9~3.1g/cm3, and the hardness is 3~5. Magnesite can be divided into two types: crystalline and amorphous according to its crystalline state. Crystalline magnesite is rhombohedral, columnar, plate-like, granular, compact, soil-like and fibrous, etc. It often contains calcium and manganese analogs. Fe2+ can replace Mg2+ to form magnesite (MgCO3). )-Siderite (FeCO3) completely isomorphic series. Amorphous magnesite has a gel structure, often spring-like, without luster, without cleavage, and has a shell-shaped section.
When magnesite is heated to above 640°C, it begins to decompose into magnesium oxide and carbon dioxide. When calcined at 700~1000℃, the carbon dioxide does not completely escape and becomes a powdery substance called light burnt magnesia (also called caustic magnesia, calcined magnesia, α-magnesium, chalcogenite), which has strong chemical activity, Has a high degree of adhesiveness, easy to react with water to generate magnesium hydroxide. When calcined at 1400~1800℃, carbon dioxide completely escapes and magnesia forms a compact periclase mass. Weigh burnt magnesia (also known as hard burnt magnesia, dead burnt magnesia, β-magnesium, dead burnt magnesia, etc.). This heavily burnt magnesia has high refractoriness. The recalcined magnesia is melted at 2500~3000℃, and after cooling and solidification, it develops into a perfect periclase crystal, called fused magnesia or molten magnesia. The high-temperature calcined magnesia is not easy to combine with water and carbonic acid and has hardness Large, strong chemical resistance, high resistivity, and other characteristics. Because these calcined products of magnesite have different chemical properties and characteristics, their uses are also different. Light burned magnesia is mainly used to manufacture cementitious materials, such as magnesium-containing cement, heat, and sound insulation building materials, and can also be used as ceramic raw materials. After the light burned magnesium is chemically treated, it can be made into a variety of magnesium salts, which can be used as raw materials for medicine, rubber, man-made fibers, and papermaking. Die-burned magnesia is mostly used as a refractory material for metallurgy, used to make magnesia bricks, chrome magnesia bricks, magnesia, and metallurgical powder. Fused magnesium oxide is mainly used as lining and magnesium crucible for medium and high-frequency induction furnaces for smelting special alloy steel, non-ferrous metals, and precious metals. It can also be used as high-temperature electrical insulation material. Magnesium metal can be extracted from magnesite by electrolysis, reduction, etc. Magnesium has the characteristics of lightweight (the weight is only 2/3 of aluminum), active chemical properties, and good electrical and heat transfer performance. It can be fused with other metals to form a variety of alloys with low specific gravity, high strength, and good mechanical properties. It is widely used in the Military industry and defense cutting-edge industry. Since magnesium is easy to oxidize and burn in the air to give off a strong light, magnesium powder can be used to make flares and incendiary bombs. Magnesium can also be used as a reducing agent for smelting titanium, zirconium, uranium, and beryllium, and as a spheroidizing agent for ductile iron and a desulfurizing agent for steel in the iron and steel industry.
Quality Standards for Magnesite Products
The particle size requirements of magnesite products are as follows:
(1) 25~100mm: no more than 15% for those smaller than 25mm, no more than 10% for those larger than 100mm, and the maximum particle size are no more than 120mm.
(2) No more than 10% for those larger than 40mm, and the maximum particle size is not larger than 60mm.
(3) 0~25mm: no more than 10% for those larger than 25mm, and the maximum particle size is no more than 40mm.
(4) 50~80mm (for reverberatory kiln roasting light-burned magnesia powder): no more than 15% for those smaller than 50mm, no more than 10% for those larger than 180mm, and the maximum particle size is no more than 200mm.
| Quality Standards for Magnesite Products | |||
| Grade | Chemical Composition Content (%) | ||
| MgO is not less than | CaO not greater than | SiO2 is not greater than | |
| Extraordinary | 47 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| First Grade | 46 | 0.8 | 1.2 |
| Second Grade | 45 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Third Grade | 43 | 1.5 | 3.5 |
| Fourth Grade | 41 | 6 | 2 |
| Magnesite | 33 | 6 | 4 |
Magnesite Flotation Process
Process introduction
Magnesite is a carbonate mineral. We mainly adopt the direct flotation process and reverse flotation process to beneficiate magnesite.
Application field
The reverse flotation process is suitable for high-grade ores with less calcium and iron (Fe). For low-grade ore, we combine these two methods. The reverse flotation process removes silicon-containing materials, while the direct flotation process removes calcium and iron (Fe)-containing materials.
Process Introduction
Magnesite flotation process-crushing and grinding process
Crushing: The raw ore (less than 200mm) is crushed to 10~0mm through a two-stage closed circuit process including a jaw crusher and a vibrating screen.
Grinding: Closed-circuit grinding of the broken ore, grind the ore to -200mm 70%, and then enter the flotation process;
Magnesite flotation process-separation stage
At this stage, the main equipment is a flotation machine, stirring tank, thickener. The following two methods are the magnesite flotation process designed by us.
High-grade magnesite flotation process
The ground ore is sent to a stirring tank and meshed with the flotation agent. Reverse flotation will get the concentrate puree. The pulp will then be transported to the thickener to reduce moisture.
Low-grade magnesite flotation process
Only the reverse flotation process is used, and the impurities in the raw ore cannot be removed. Therefore, for low-grade magnesite, we usually combine two methods, namely reverse flotation process (one roughing-one cleaning) and direct flotation process (one roughing-one cleaning). In the reverse flotation process, part of the tailings is separated, and at the same time, the concentrate and intermediate products are obtained by direct flotation.
LATEST PRODUCTS
Twin Screw Feeder
【Feeding Capacity】 10-160 t/h【Power】 2.2-…
Tubular Screw Conveyor
【Capacity】6-50 m3/h【Procesible Material】 …
Heavy Plate Feeder
Capacity: 100-240 m3/h Power: 15-45 kW Speed: 0…