Type
Mineral
Mineral Classification
Oxide
Chemical Formula
TiO2
Streak
Bright red to dark red
Mohs Hardness
6.0 – 6.5


Type
Mineral
Mineral Classification
Oxide
Chemical Formula
TiO2
Streak
Bright red to dark red
Mohs Hardness
6.0 – 6.5
Crystal System
Tetragonal ditetragonal dipyramidal
Color
Reddish brown, red, pale yellow, pale blue, violet, rarely grass-green, or black
Luster
Adamantine to submetallic
Fracture
Uneven to sub-conchoidal
Rutile is nature’s most common and stable form of titanium dioxide. It forms under high pressure and high temperature in igneous and metamorphic rocks. It is a key ingredient in paint and a useful component in optical equipment.
Rutile is recovered through surface mining and dredging of dense beach sands.
Because it has a very high index of refraction, rutile is used for many purposes in optics, most of which come from synthetic rutile, first produced in 1948. As a source of titanium dioxide pigment, rutile is used in plastics, paper products, paints, sunscreen, and even food coloring. Certain welding equipment also uses it.
Generally, use gravity separation to throw away a part of low-density minerals or fine mud and carry out preliminary enrichment of rutile. The commonly used gravity separation equipment includes the spiral chute and shaker.
Rutile is a non-magnetic mineral, while garnet and tangerine, which are often associated with it, are magnetic minerals. Hornblende and epidote are weak magnetic minerals, so they can be separated by a combination of weak magnetic separation and strong magnetic separation. In the magnetic separation process, the weak magnetic drum magnetic separator is used for separation first to remove a small amount of strong magnetic minerals in the ore and to prevent the strong magnetic minerals from damaging the high gradient magnetic separator in the subsequent strong magnetic separation process.
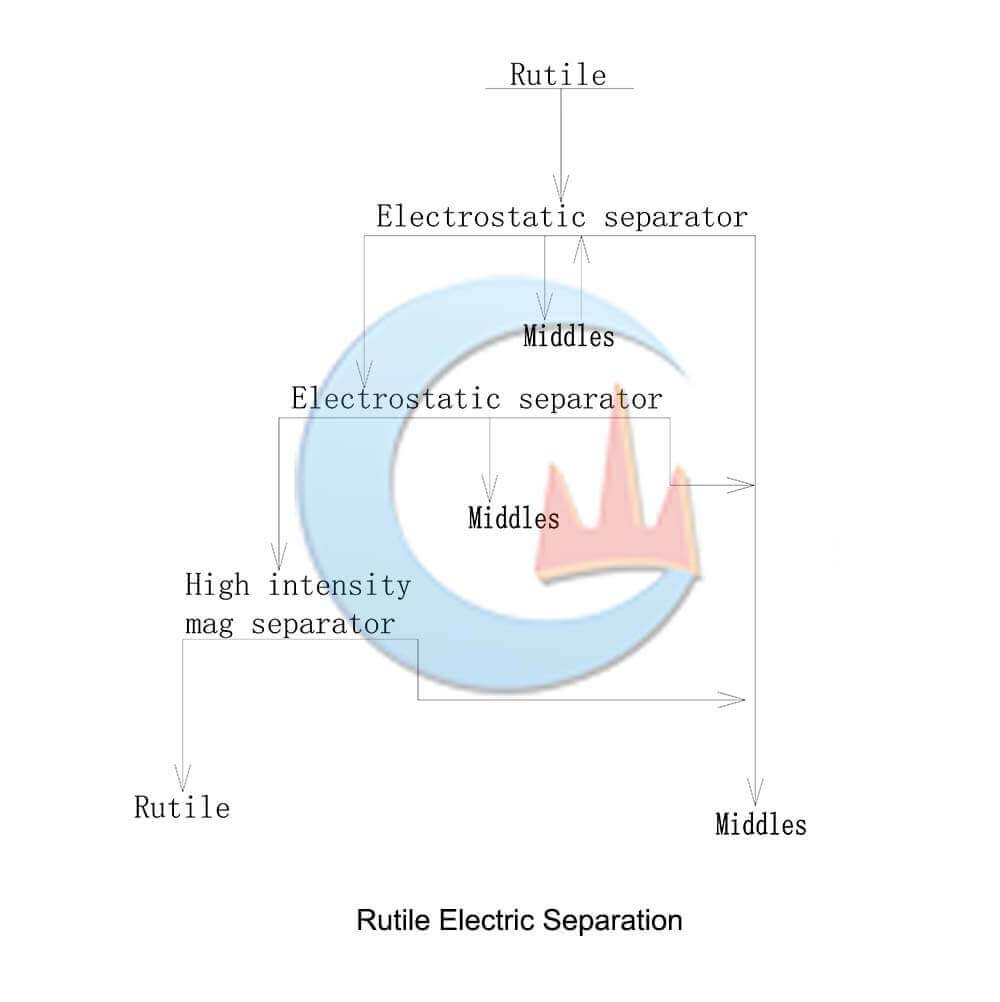
Rutile is a good conductor of electricity, with a resistivity of only 102-10 Q-m. At the same time, minerals such as silicate and zolite are non-conductors, with a resistivity of more than 1000 Q-m, so they can be separated by electrical separation.
Flotation is an effective method for separating fine-grained rutile and reducing metal loss.
Since the rutile concentrate product requires S≤0.05%, the titanium dioxide content is required to exceed 87.5%, and the rutile single mineral content of the rough concentrate is only More than 60%, there are many impurity minerals such as silicate, carbonate, iron minerals adhered to the edges and cracks of rutile. In order to remove these impurities and improve the quality of the concentrate, the pickling process must be adopted.
If you have some questions about our products, please feel free to fill out the form below, and we will contact you within 24 hours. Rest assured that we won’t reveal your information to anyone.