Flotation equipment is an indispensable part of beneficiation. Choosing a suitable flotation machine and the correct operation process can improve the flotation effect and save enterprises’ costs. During the use of the flotation machine, a certain amount of medicament should be added to complete the flotation operation with the help of the medicament. For the use and addition of pharmaceuticals, it needs to pay attention to many points. The following will introduce the foaming agent in detail.
Foaming Agents
The foaming agent is a surface active substance that mainly reduces the interfacial tension at the air-water interface, promotes the formation of tiny bubbles in the slurry, expands the sorting interface, and ensures that the bubbles rise to form a foam layer. In other words, it can promote the formation of a large amount of foam of suitable size and certain stability in the medium. These substances with foaming effects are called foaming agents.
The foaming agent is a heteropolar organic substance. The polar group is hydrophilic, and the non-polar group is aerophilic. It aligns the foaming agent molecules at the interface of air and water. Most foaming agents are surface-active substances that strongly reduce the surface tension of water. The surface activity of the same series of organic surfactants increases according to the “one-third” rule, which is the so-called “Tefonbe rule.” The foaming agent should have good solubility. The foaming agent’s solubility greatly influences the foaming performance and the characteristics of forming bubbles. If the solubility is high, the consumption of the drug will be large, or a large amount of foam will occur rapidly, but it cannot be durable. The ice will not dissolve in time when the solubility is too low. With the loss of foam or the slow foaming speed, the duration is long and difficult to control.
Classification of foaming agents
(1) Classification according to the source of the drug
- Natural product extraction: pine oil, camphor oil.
- Extraction of by-products of coal char industry: methanol, pyridine.
- Human synthesis, alcohols, ethers, alcohol ethers.
(2) Classification according to the characteristics of molecular structure
- Non-ionic (alcohols, ether alcohols, ethers, esters).
- Ionic type (phenols, double pyridines, hydrocarbyl sulfonic acid (sulfuric acid) salts, carboxylic acids, and their soaps, amines).
Application and Attention of Foaming Agent
The Function and Mechanism of The Foaming Agent
1. Reduce the gas-liquid interface’s tension and change the air bubbles’ dispersion
(1) Relationship between δAW and foaming ability
Under the same external power consumption condition, the δAW decreases, the airflow is divided and easy to form bubbles, and more gas-liquid interfaces are generated, which are beneficial to the separation.
The relationship between the two is as follows
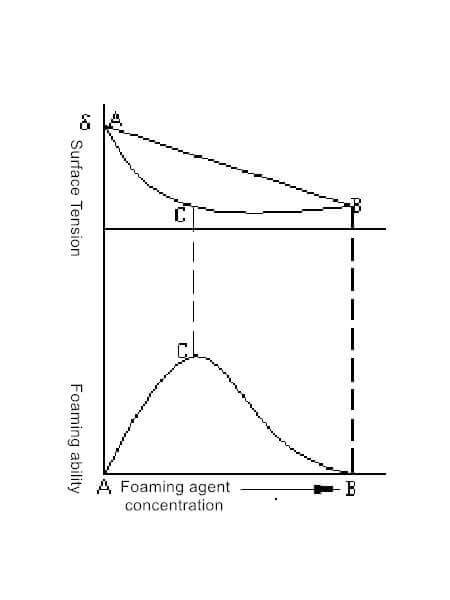
In conclusion:
- Foam and state cannot form a stable foam layer, which is much lower than the value of point C in actual production.
- The size of the foaming ability is not entirely determined by the absolute value of the surface tension reduction.
(2) Improve the dispersion of bubbles
At a certain amount of inflation V, the smaller the bubble diameter, the larger the gas-liquid separation interface area, and the higher the dispersion of the bubbles in the separation space, which is beneficial to the separation.
Requirements for bubble size: Determine the bubbles’ size according to the sorting requirements on the buoyancy and the lifting speed. There is no foaming agent in the clear water, and the diameter of the generated bubbles is 4-5mm. When there is a foaming agent, the diameter of the bubbles is 0.8-1mm.
Modern theoretical studies have shown that microbubbles have a strengthening effect on the flotation process.
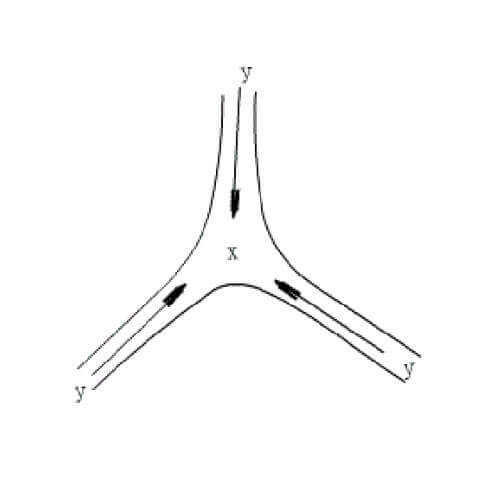
2. Block or mitigate the bubbles’ mutual merger (extinguish)
(1) Reasons for the merger (disappearance) of bubbles
- Dehydration
Gravity: water leaks from the foam layer;
Evaporation: the surface water of the foam layer evaporates;
Tension effect: △Px= -2δ/R<0
In the Pulandai border area: △Py=0
- Capillary pressure: different diameters of adjacent bubbles have different capillary pressures P. The bubbles penetrate the large bubbles and are absorbed by the large bubbles.
(2) Mechanism of action
- The directional arrangement of surfactants at the liquid surface interface forms a hydration film, which hinders the flow and evaporation of water and improves the life of the bubbles.
- Electricity: The same kind of electricity repels each other, which is difficult to approach.
3. Increase the mechanical strength of the bubbles and improve their stability
When the bubble is subjected to external force, it deforms locally, the surface area increases, the concentration of the foaming agent in the deformation area decreases, and the tension increase so that the bubble returns to its original shape.
4. Reduce the floating speed of bubbles in the pulp
Reason
- The open shape of the floating bubble
Without foaming agent: oval, fish shape
With foaming agent: round
- The cohesive attraction of water dipoles.
- The bubble’s diameter is small, and the buoyancy and speed are reduced
Function
- Increase the probability of collision between bubbles and ore particles.
- Reduce collision kinetic energy.
- Reduce the vibration and vibration of mineralized bubbles and reduce the probability of falling off.
The role of the foaming agent to form
- The role of the simple foaming agent;
- Coadsorption of blowing agents and collectors.
The stability of the foam layer
- Instability of two-phase foam layers
- Stability of three-phase foam
- The armoring effect of ore particles;
- The effect of the agent, the coadsorption of the foaming agent, and the collection;
- The influence of particle shape and size.
- Secondary enrichment
Influence of composition and structure of foaming agent on foaming performance
- The effect of polar groups on foaming performance
- Affects solubility;
- Affect the degree of dissociation;
- The effect of hydration.
- The effect of non-polar groups on foaming performance
- Carbon chain length;
- Non-polar base properties, structural properties, degree of saturation, and chain form.
The Role of Foaming Agent in The Flotation Process

1. The foaming agent molecules prevent the merger of bubbles.
Various foaming agent molecules have the effect of preventing the merger of bubbles. The order from strong to weak is polyethylene glycol ether > Triethoxybutane > octanol > C6-Ca mixed alcohol > cyclohexanol > cresol.
2. The foaming agent reduces the speed of the upward movement of the bubbles.
The test shows that the bubble rising rate becomes slower after adding the foaming agent. The effect of the flotation agent on the rising speed of bubbles: But xanthate is 100%, then the relative percentage of bubble rising rate of other foaming agents is
Phenol 93.4%
Cresol 90.8%
Pine oil 88.3%
Cyclohexanol 88.2%
Dimethylphthalic acid 80.7%
Heptanol 76.8%
Octanol 75.8%
Ethanol 76.2%
Tetrapropylene glycol methyl ether 72.9%
Triethoxybutane 72.3%
A possible reason why the blowing agent slows the rise of the bubbles is that the blowing agent molecules form an “armor layer” on the surface of the bubbles. This layer is attractive to the water dipole, and at the same time, the double-as-water film is easy to deform with the resistance, thus blocking the upward movement.
3. The foaming agent affects the size and dispersion state of the bubbles.
The size and composition of the bubble particle size directly impact the flotation index. Generally, the average diameter of the bubbles generated in the pure water by the mechanical stirring flotation machine is 4-5mm. After adding the foaming agent, reduced the average diameter to 0.8-1 mm. The smaller the bubbles, the larger the flotation interface, which is conducive to the adhesion of ore particles. However, for the bubbles to float up with the ore particles, they must have sufficient buoyancy and an appropriate floating speed. Therefore, it is not that the smaller the bubbles, the better, but the proper size and particle size distribution.
4. Interaction between foaming agent and collector.
In the flotation process, the interaction between the frother and the collector is of great significance to the flotation. Some foaming agents have both collecting properties, such as sodium alkyl sulfonate, cresol, bipyridine, etc., While some collectors have both foaming properties, such as tar oil, oxidized paraffin soap, etc.
LATEST PRODUCTS
Heavy Plate Feeder
Capacity: 100-240 m3/h Power: 15-45 kW Speed: 0…
Plate Magnetic Separator
【Capacity】8-35 t/h 【Power】1.5-3 kW 【Applic…
Slurry Magnetic Separator
【Capacity】10-100 m3/h 【Feeding Material Densi…