Molybdenum is an important rare metal and strategic reserve resource, the average content of which is only 1/100,000 in the earth’s crust. It has excellent properties, such as high melting point, high temperature resistance and good thermohardness, etc., and is widely used in machinery manufacturing, metallurgy, electronics, shipbuilding, chemical industry, aerospace and other industries”. Molybdenite is the most important source of molybdenum extraction Molybdenite, except for a very small number of single deposits, is widely associated with sulfide minerals, especially copper sulfide minerals. According to statistics, nearly 75% of copper and 50% of molybdenum in the world are produced from copper-molybdenum ores. 12.31 The porphyry-type copper ore is the main type of copper-molybdenum ore, in which copper-molybdenum mainly exists in the form of chalcopyrite and molybdenite. This type of ore has the characteristics of dense structure, fine particle size, etc., and the wettability between the two small difference. The buoyancy is relatively close, making it difficult to separate the two. Copper-molybdenum separation has become an important and difficult problem in the field of mineral processing. Researchers at home and abroad have done a lot of research work in the field of copper-molybdenum separation.

There are two common methods for the separation of copper and molybdenum, one is floating molybdenum to suppress copper, and the second is floating copper to suppress molybdenum. Among them, floating molybdenum and suppressing copper are the most important mineral processing methods at present.
The inhibitor schemes for the separation of copper and molybdenum by floating molybdenum to suppress copper include:
- Sodium sulfide method;
- Sodium sulfide + steam heating method;
- Single cyanide method;
- Cyanide + sodium sulfide method;
- Knox agent (or its combination with sodium cyanide) method;
- ferricyanide and ferrocyanide method;
- Sodium hypochlorite or hydrogen peroxide method;
- Organic inhibitor method such as mercaptoethanol.
Separation of copper and molybdenum: Sodium sulfide, cyanide, arsenic or phosphonox agents are more effective in inhibiting copper minerals mainly composed of chalcopyrite and bornite; ammonium sulfide, ferricyanide and ferrocyanide, oxidants, secondary Chlorate and hydrogen peroxide are more effective in inhibiting secondary copper sulfide minerals. Organic inhibitors such as mercaptoethanol are newly developed non-toxic and efficient molybdenum associated sulfide inhibitors, which are being promoted.
The measures improve the separation effect of copper and molybdenum
(1) Concentration and drug removal
Before the separation of the mixed concentrate, concentration and drug removal are carried out to remove the excess chemicals entering the mixed concentrate, so as to ensure that the stirring and roughing are carried out at an appropriate concentration.
(2) Steam heating
Some foreign copper-molybdenum beneficiation plants heat the copper-molybdenum mixed concentrate with steam (85-90°C) before the separation of copper-molybdenum, and sometimes add an appropriate amount of lime (0.8-1.2kg/t concentrate), and blow in oxygen or air . Its purpose is to destroy the collector film on the surface of the mixed concentrate by desorption and decomposition. Many countries regard the sodium sulfide + heating (steam blowing) method as the best solution for the separation of copper and molybdenum concentrates. This method uses sulfide to suppress copper minerals and directly heats them with steam along the flotation line. (60-75°C) pulp, which not only accelerates the desorption and decomposition of the collector, but also slows down the oxidation of sulfide, greatly reduces the amount of sulfide, and improves the separation index.
(3) Add sodium sulfide in stages
The sodium sulfide method is the most commonly used method for the separation of copper and molybdenum. It can inhibit all metal sulfide minerals other than molybdenum. It is more beneficial to add sodium sulfide in stages. A part of the sodium sulfide solution is often added to the stirring tank, while the other part of the sodium sulfide is placed in the rough and selected foam tank in solid form, and the heat generated when the sodium sulfide dissolves is used to make the The temperature of the pulp is increased to enhance its inhibitory effect.
(4) Use nitrogen flotation
The inhibitors used in copper-molybdenum separation flotation, such as sodium sulfide, sodium sulfite, sodium sulfide or phosphorus pentasulfide in Knox reagent, are easy to oxidize and lose their inhibitory effect. Due to the separation cycle of copper and molybdenum, the number of selections is large (6-8 times), and the operation line is long, the increased consumption of these chemicals due to oxidation is more prominent. In order to avoid chemical oxidation and reduce the dosage, the copper-molybdenum separation plant uses nitrogen instead of air as the inflated medium for copper-molybdenum separation and flotation, which has achieved remarkable economic results, which can reduce the dosage of phosphonox by 50%.
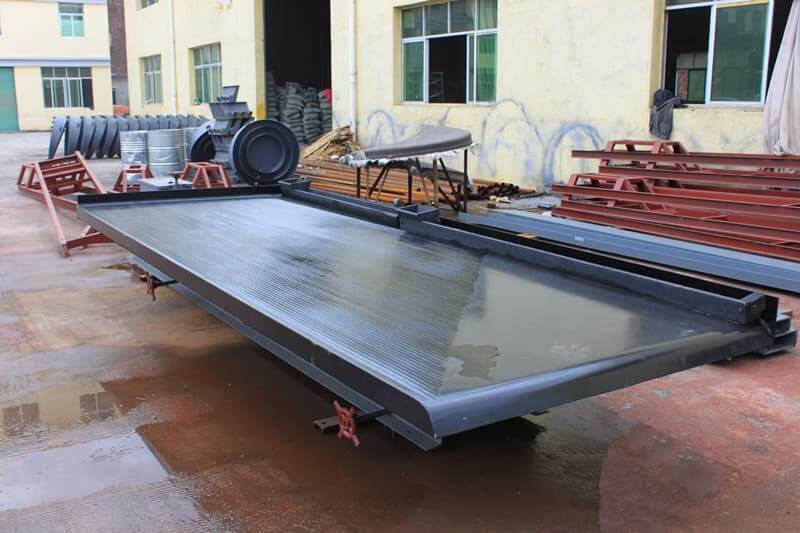
Copper and Molybdenum Separation Equipment
LATEST PRODUCTS
Twin Screw Feeder
【Feeding Capacity】 10-160 t/h【Power】 2.2-…
Tubular Screw Conveyor
【Capacity】6-50 m3/h【Procesible Material】 …
Heavy Plate Feeder
Capacity: 100-240 m3/h Power: 15-45 kW Speed: 0…