Gold-sulfur separation is a process that separates gold and sulfur from ores that contain gold and sulfur. This process is commonly used in the extraction and refining of gold deposits. Here are some standard gold-sulfur separation methods.
Gold-Sulfur Separation Method
Thermal treatment
The first step in gold-sulfur separation is usually a high-temperature treatment to break down the sulfide ore and separate the sulfur from the gold. We accomplish this by heating the ore to high temperatures, causing the sulfides to break down into sulfur gas (hydrogen disulfide or hydrogen sulfide gas) and metals.
Oxidation
The sulfides in some gold ores can be converted into oxides or sulfates through an oxidation reaction, thereby separating the sulfur from the gold. We can achieve this by using oxidizing agents such as oxygen or chemicals.
Flotation
Flotation is a physical method that separates gold from mixtures containing gold ore. During flotation, the ore is finely crushed and mixed into the water. Then, a special chemical is added that causes the gold particles to attach to the bubbles and rise to the surface while sulfur and other impurities sink.
Dissolution and Extraction
We can isolate sulfur by dissolving the ore in an acidic or alkaline solution while extracting gold by selective solvent extraction.
Atmosphere furnace treatment
During the gold-sulfur separation process, an atmosphere furnace is often used to heat the ore and control the atmosphere to achieve sulfur decomposition and gold extraction.
Please note that the specific method of gold-sulfur separation will vary depending on the type of ore, the concentration of gold, and the physical properties of the ore. Different ores and process conditions may require different separation methods. In addition, the gold-sulfur separation process usually requires strict environmental protection measures to reduce environmental negative impacts. Therefore, relevant regulations and standards must be followed when mining and processing gold.
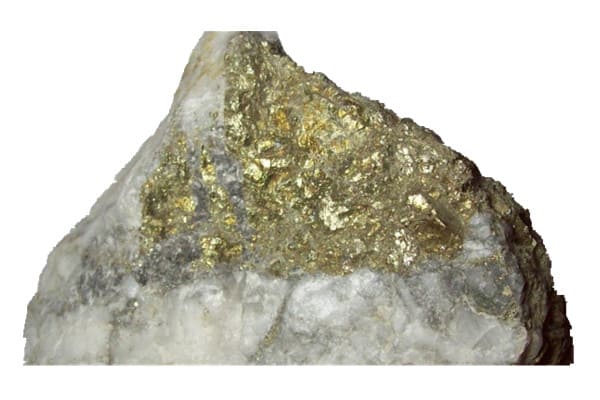
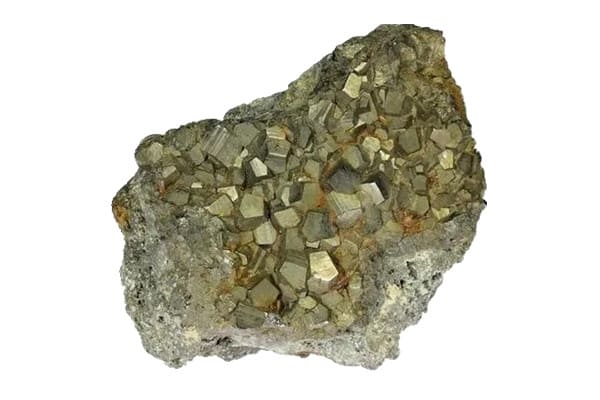
Pyrite
Pyrite is a common gold-bearing mineral widely distributed in my country and has significant reserves. In non-ferrous metal beneficiation, pyrite concentrate is usually called sulfur concentrate. Gold in gold-bearing pyrite is mainly dispersed in microscopic, submicroscopic, and lattice gold, and it is challenging to process gold ore. As China’s easy-to-process metallurgical ore reserves continue to decrease, how to efficiently extract gold from refractory gold ores has become a significant issue facing the current gold industry.
Pyrite Processing Plant
Ore information: The mineral ores contain 35.68% sulfur, 29.24% iron, and 3.65g/t gold, with a high extraction value.
According to phase analysis, the gold in the ore mainly exists as gold sulfide, gold oxide, and gold silicate. We must destroy the pyrite crystal structure in the sample to fully expose the gold mineral before we can recover the gold.
Pretreatment Process
The pretreatment process of pyrite is oxidative roasting-acid dissolution, wet acidic oxidative decomposition, and wet alkaline oxidative decomposition. After the sulfur concentrate is pretreated, a cyanide agent extracts gold from the gold concentrate obtained after the pretreatment.
Optimal Conditions for Oxidation Roasting-acid Dissolution
The best conditions for oxidation roasting-acid dissolution are:
- Roasting temperature 700°C, roasting time 3 hours;
- Acid dissolution at room temperature, liquid-to-solid ratio 2ml/g, stirring, sulfuric acid dosage of 20% of the roasting residue mass, and acid dissolution time of 8 hours.
Under optimal conditions, the average yield of gold concentrate is 52.4%, all gold is concentrated into gold concentrate, and the gold grade can reach 6.79g/t. We used this gold concentrate as a gold leaching sample and a cyanide gold leaching agent to conduct the test. The optimal gold leaching conditions were: normal temperature, gold leaching agent dosage 0.04%, leaching time 12h, liquid-to-solid ratio 3ml/g, pH value 11, stirring speed 400r/min. Under the optimal gold leaching conditions, the average leaching rate of Au in the gold concentrate after oxidation roasting and acid dissolution treatment was 89.6%.
Optimal Conditions for Wet Acid Oxidation Decomposition
The optimal conditions for the wet acid oxidation decomposition test are:
The sample grinding fineness is 95%-200 mesh, the Fe3+ dosage is 50% of the theoretical dosage, the hydrogen peroxide dosage is 120% of the theoretical dosage, and the sulfuric acid dosage is 100% of the theoretical dosage. The reaction temperature is 95°C, the reaction time is 8 hours, the liquid-to-solid ratio is 6 ml/g, and the stirring speed is 400 r/min. Under optimal conditions, gold concentrate with a gold grade above 9g/t was obtained. Under optimal gold leaching conditions, the average Au leaching rate was 87.4%.
Optimal Conditions for Wet Alkaline Oxidation Decomposition
The optimal conditions for the wet alkaline oxidation decomposition test are:
Stirring and aeration reaction at room temperature for 7 days, the sample grinding fineness is 95%-200 mesh, the NaOH dosage is 100% of the theoretical dosage, and the liquid-to-solid ratio is 3ml/g. Under optimal conditions, the gold concentrate’s average recovery rate is 96.35%, and the average gold grade is 6.71g/t. Under optimal gold leaching conditions, the Au leaching rate was 82.2%.
For gold-sulfur separation, pyrite beneficiation, and other mineral beneficiation processes, please consult jxsc.
LATEST PRODUCTS
Twin Screw Feeder
【Feeding Capacity】 10-160 t/h【Power】 2.2-…
Tubular Screw Conveyor
【Capacity】6-50 m3/h【Procesible Material】 …
Heavy Plate Feeder
Capacity: 100-240 m3/h Power: 15-45 kW Speed: 0…