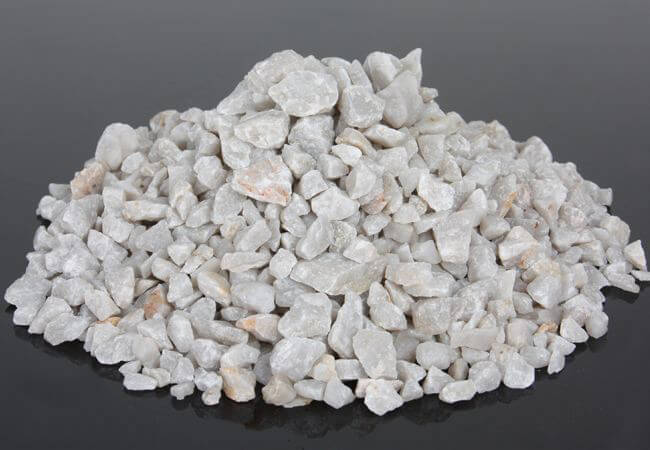
Silica Sand Processing Plant
High-grade quartz/ silica sand is litter in nature, silica ore contains many kinds of impurity minerals, objectively leads to the difficulty in purifying quartz sand. Silica sand processing plant research does a positive influence on technology for developed high-quality quartz sand products to meet high-tech silicon.
The grade of Brazil silica mine ore SiO2 is generally above 93%, and it is currently only used as quartz fertilizer for chemical fertilizers. In order to further improve the utilization value of the quartz sand ore and make it have better economic development and utilization value, on the basis of the research of process mineralogy, the quartz selection exploration test is carried out in order to increase the SiO2 content and reduce the impurities A1203, Fe203 and Ti. The content of the refined quartz sand grade can be selected to provide technical support for improving the utilization value of the mine.
1 Description of silica ore
1.1 Chemical composition of silica ore
Quartz ore is dominated by SiO2, and the remaining components are very low. Al2O3, K2O and iron are high in content and, in addition, contain a certain amount of CaO, MgO and Na2O, so the main purpose of the purification test is to remove Al2O3, K2O and iron.
| Content | SiO2 | K2O | Na2O | CaO | MgO | TFe2O3 | Al2O3 |
| % | 93.42 | 0.97 | 0.14 | 0.42 | 0.17 | 0.99 | 2.57 |
1.2 Content of mineral
The surface of ore is colorless under the naked eye, and the ore structure is mainly blocky. The main mineral is quartz, and the impurity minerals are mainly high-alumina minerals such as clay and potassium feldspar and iron minerals.
| Mineral | Hematite | Muscovite | Quartz | Clay | Hydromica | Felspar | Tourmaline |
| Content | <1 | 1 | 75-80 | 10-15 | 2 | <5 | <1 |
1.3 Mineral existing forms
Quartz: The main carrier mineral of SiO2 is also the main purpose mineral of the experimental research. Its form and embedding form are simple. The output forms in the ore are mainly the following: (1) Sand: sub-circle-sub-angled Chips, good sorting, particle support, pore-contact cementation, mostly in the form of fine-medium grain sand of 0.1-0.5mm. (2) Siliceous agglomerate: Clay recrystallized product. (3) Increase the edge shape: it is the recrystallized product of silicon matter between quartz crumbs, which is secondary to increase the distribution of quartz crumbs around the edges. Clay, K-feldspar: mainly minerals for K2O and Al2O3, K-feldspar is sub-circular-sub-horny crumb, mostly fine-medium-grained sand of 0.1-0.5mm; amorphous cryptocrystalline is Mainly, partially crystallized into microscopic scale-like hydromica. Hematite: It is an iron mineral in ore that is distributed in the inter-debris pores with 0.002 mm ± particles.
1.4 The embedding grain size of quartz sand
In order to formulate a reasonable beneficiation process and determine the appropriate grinding fineness, the grain size of quartz in the ore was counted. The results show that the quartz grain size in the sample is concentrated and evenly distributed in fine particles (0.417~0.104mm). The scope of the inlay.
In summary, the ore is a fine-medium-grained siliceous quartz sandstone, and the SiO2 content in the ore is only about 93%. As a refined quartz sand raw material, it needs to be purified and used. Clay minerals, potassium feldspar, and particulate iron minerals (hematite, magnetite) produced in the form of intergranular pore interstitials in the ore lead to higher levels of harmful impurities such as Al2O3, K2O and Fe. The grain size of quartz sand in the ore is 0.1-0.5mm, and the fineness of grinding is -0.1m (140 mesh) to ensure that about 60% of the quartz in the ore sample dissociates. Although the ore sample is an optional quartz sandstone ore, the physical properties such as specific gravity of potassium feldspar are similar to those of quartz, and it is difficult to separate from quartz.
2 Silica beneficiation process
The mineralogical study of quartz sand ore shows that impurity minerals mainly exist between the surface of the particles and the cracks of quartz particles. Quartz surface is unclean, distributed with a lot of dusty clay and impurity minerals, mostly secondary cementation, local clay cementation, a very small amount of quartz crystals containing gas-liquid inclusions, other mineral inclusions, but generally within the quartz crystal Basically purer. The impurities of ore mainly come from clay minerals, iron minerals, potassium feldspar, and a small amount of clay derived from the submicroscopic distribution of secondary quartz cement and primary quartz particles. Based on this, the process of grading-wiping mud-acid treatment was selected, and the single-factor beneficiation and purification test of the quartz sand was carried out, and the feasibility of magnetic separation and flotation to remove potassium and aluminum was explored.
2.1 Grinding size
the quartz grade doesn’t significantly increase under very fine or coarse particle size conditions, when the size is -0.208~+0.104mm, the silica grade increase to 95.06%, besides, the total content of Fe, Al and Ti is also at the smallest point, suggesting that the quartz and impurity minerals are largely separated at the grade. For the economics of the grinding process and the classification effect of grinding, choose -0.208~+0.104mm as the suitable grinding size. quartz rock crusher for sale
2.2 Desliming
Because the impurities in the quartz ore adhere to the surface, the rubbing agent can clean the surface impurity thus increase the SiO2 grade. click to know the desliming machine price.
2.3 Acid treating
Because the acidic medium has good leaching power for Fe, Al, K, etc., but it has no effect on Si. The sample is treated with monoacid (sulfuric acid), and the SiO2 grade up to 99%, and the harmful impurities such as Al2O3 and TFe2O3 are greatly increased. Reduced refined quartz sand, and with the increase of treatment time, the impurity removal rate increased significantly; although hydrofluoric acid (HF) has a certain etch on SiO2, it has been proved by experiments that the mixed acid treatment effect of adding HF under the same conditions Better than monoacid, a reasonable balance can be obtained between the promotion of SiO2 and the reduction of Al2O3 and TFe2O3.
2.4 Removal of iron and potassium
Considering that remove magnetic mineral before acid treatment can reduce the consumption of acid. But test shows that the use of strong magnetic separation cannot achieve the purpose of effective iron removal.
The impurities K and Al in the ore are mainly derived from potassium feldspar and clay, silica washing process can remove some clays. in order to do further research, the particle size after deliming treatment is -0.208~+ The 0.104mm sample was subjected to a flotation process exploration test to separate the feldspar and quartz by flotation. The flotation test was carried out by adding a collector under normal temperature (18-20 °C) acidic environment.
3 Conclusion
3.1 Quartz sand beneficiation purification method and process flow are generally considered from three aspects: the occurrence state of impurity minerals in the ore, the ore dressing cost of the purification process, and the industrial use of the fine sand product. Under the premise of satisfying industrial use, Whenever possible, choose a process that is simple in process, low in cost, and easy to implement in an industrial manner.
3.2 Through a reasonable and simple process, the SiO2 in the ore can be purified to more than 99%. The mixed acid treatment effect of adding HF is obviously superior to that of monoacid (sulfuric acid), but the problem of F emission in the leachate needs to be considered.
JXSC provides silica sand processing plant equipment, silica washing machine, stone crusher, magnetic separator, flotation, etc. Contact us to know more info about the silica mining process.
You may interest in the silica sand processing solutions
LATEST PRODUCTS
Twin Screw Feeder
【Feeding Capacity】 10-160 t/h【Power】 2.2-…
Tubular Screw Conveyor
【Capacity】6-50 m3/h【Procesible Material】 …
Heavy Plate Feeder
Capacity: 100-240 m3/h Power: 15-45 kW Speed: 0…