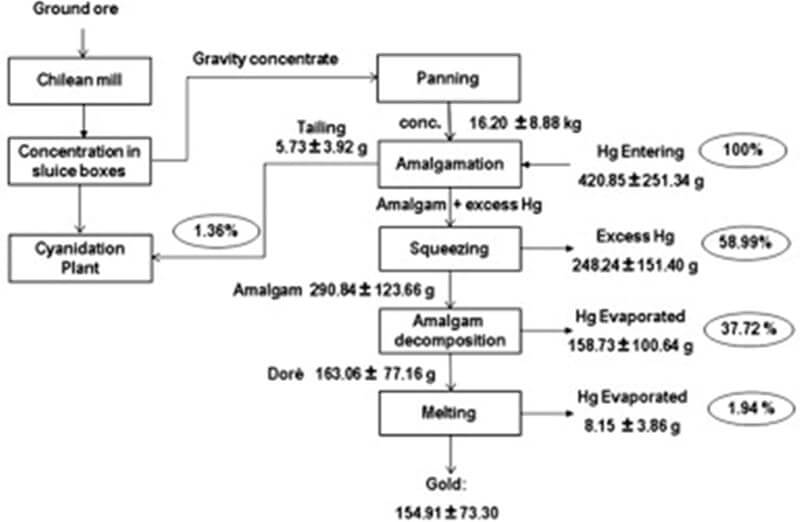
Gold extraction with mercury is an ancient method for gold separation. It refers to the chemical beneficiation method of wetting gold particles in ore slurry with liquid metal mercury to form an amalgam, so as to separate gold particles from other metal minerals and gangue This ancient gold extraction method has been gradually replaced by cyanide leaching and flotation in modern times, but amalgamation is still the main method in recovering dissociated monomer natural gold, especially dissociated coarse-grained natural gold.
Is mercury still used in gold mining?
Most large-scale and regulated gold mining companies do not use mercury in their mining operations. However, Small-scale and illegal gold mining operations will sometimes use mercury to separate the gold from other materials. In order to protect the environment from pollution and protect the health of workers, the use of mercury should be limited. Some foreign countries have banned the use of mercury mixing, but only some gold mines and some local small mines are still using mercury mixing in the world. So there are still a small number of small mines that use amalgamation to select gold.
Amalgamation can be divided into internal and external amalgamation according to its production model. Amalgamation is widely used to separate gold and heavy sand minerals in placer gold mines; In vein gold mines, amalgamation is usually used as a part of the combined process, combined with flotation, gravity separation, and cyanidation, which is mainly used to promote the collection of coarse-grained monomer gold.
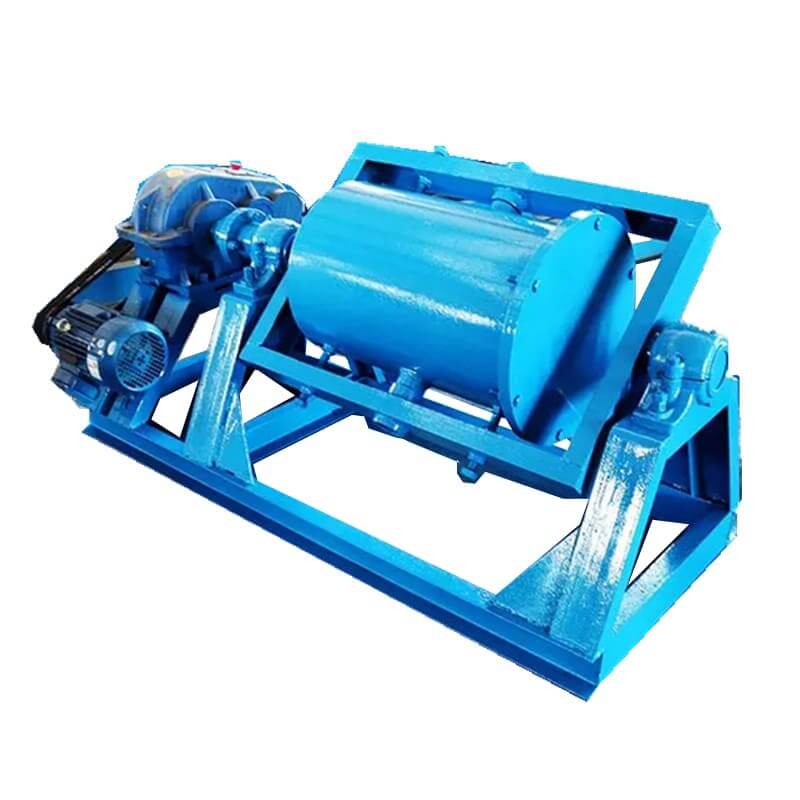
Internal amalgamation is carried out in the mercury mixing cylinder or grinding machine, which can better control mercury pollution.
The main equipment of external amalgamation is a mercury mixing plate, which is composed of support, bed surface, and mercury plate. Mercury plate materials include copper plates, silver-plated copper plates, and mercury plates, and the mercury mixing effect of the silver-plated copper plate is the best. In order to facilitate silver plating and replacement in production, electrolytic copper plates are often cut into small pieces with a width of 400 ~ 600mm and a length of 800 ~ 1200mm. After silver plating, they are laid on the bed surface one by one according to the inclined direction of the support.
The determination of mercury plate area is related to the amount of ore processed, the nature of the ore, and the role of the mercury mixing operation in the gold separation process. Generally, when the slurry flow depth on the mercury plate surface is 5 ~ 8mm and the flow rate is 0.5 ~ 0.7m/s, the mercury plate area required for processing a ton of ore is 0.05 ~ 0.5m2/t · day. If the mixed mercury is only to collect large particles of free gold, and the tailings still need flotation, gravity separation, and cyanidation, the public quota can be set as 0.1 ~ 0.2 m2 / ton Day.
Amalgamation operation conditions: feed concentration 10 ~ 25%, feed particle size 3 ~ 0.4mm, pulp flow rate 0.5 ~ 0.7m/s. Mercury consumption is 3 ~ 8 g / T.
Mercury reading protection: mercury can invade the human body through the skin, mucous membrane, and respiratory tract in the form of liquid, salt, and steam. Mercury can accumulate in kidneys, liver, brain, lungs, bones, and other organs and cause poisoning. In particular, mercury vapor is the most harmful to people and can cause acute or chronic poisoning. China stipulates that the content in the air is not allowed to exceed 0.01 ~ 0.02 mg / m3, and the maximum allowable concentration of mercury and its compounds in industrial wastewater is 0.05 mg / L.
Protection against mercury poisoning
- Formulate a strict mercury mixing operation system. Mercury containers shall be sealed to prevent the mercury vapor from overflowing; Wear protective articles when mixing mercury to avoid direct contact between mercury and skin; Do not store food, eat or smoke in rooms with mercury.
- The ventilation of the mercury mixing workshop and alchemy room shall be strengthened, and the washing of mercury paste shall be carried out in a closed operation cabinet with a ventilation device.
- The ground of all plants with mercury operation shall be built with materials that do not absorb mercury. The ground shall be made into a slope of 1 ~ 3%. The wall and ground shall be kept smooth and washed regularly with soapy water or potassium permanganate solution (1:1000).
- Mercury collecting devices shall be set under the operation cabinet and in the outdoor sewage well to avoid mercury loss as far as possible.
- Workshops operating with mercury should be purified regularly by the manganese dioxide absorption method, which can absorb 99% of mercury vapor in the air.
Internal Amalgamation
Internal amalgamation refers to the method of extracting gold by mixing mercury while crushing the ore in the grinding equipment. Grinding equipment is usually a disc rolling machine, tamping machine, mixing water drum or special small ball mill, rod mill, etc.
The operation process of gold extraction by internal amalgamation is: add mercury liquid while adding ore in the grinding process, mix the ore with mercury while grinding, and the newly exposed gold particles will be mercurial by contacting with mercury. After internal mercury mixing, the pulp and mercury paste is discharged by the internal mercury mixing equipment, and then the mercury paste is separated by the catcher, chute, classifier, etc.
The main disadvantage of internal amalgamation is the pulverization of mercury. When the ore is crushed, mercury is divided into particles. These particles are wrapped and covered by oxide film, lubricating oil film, and slime particles of base metals, thus losing the ability to combine with each other and causing pulverization. Powdered mercury is difficult to separate from the treated ore. most of the powdered Mercury will be lost and some gold will be taken away.
When the content of copper, lead and zinc minerals in gold-bearing ores is very small, there is no sulfide that is easy to pulverize mercury, and the embedded particle size of gold is large, the internal amalgamation is often used. Placer gold mines also use internal amalgamation to separate gold from other heavy minerals.
External amalgamation
External amalgamation refers to the method of mercury mixing and gold extraction outside the grinding equipment.
Mercury mixing plate is commonly used for gold extraction by external amalgamation. Mercury mixing plates are fixed and vibrating. There are three types of fixed mercury mixing plates: plane type, stepped type, and type with intermediate capture ditch. At present, fixed plane mercury mixing plates are mostly used in China. The plane-fixed mercury mixing plate is composed of support, a bed surface, and a mercury plate. The support and bed surface can be made of wood or steel, and the bed surface must not leak pulp. The mercury plate on the bed surface is the silver-plated copper plate, which is 3 ~ 5mm thick, 400 ~ 600mm wide, and 800 ~ 1000mm long. The mercury plates are connected to the bed surface one by one according to the inclined direction of the support.
The operation process of gold extraction by external amalgamation is: the mercury solution will be coated on the silver plating surface of the mercury plate, and the pulp will flow through the plate surface and come into contact with mercury. After starting the operation, mercury is added to the pulp. After the mercury mixing operation has been carried out for a period of time, it is convenient to retain a layer of mercury paste on the mercury surface and scrape it off in time.
The external amalgamation is suitable for the treatment of gold-bearing polymetallic ore, which is mainly used to capture coarse-grained gold. Most of the free mercury products are installed in the rough ore collection plate of the ball mill, and the gold products are mostly discharged in the rough ore collection plate of the ball mill.
LATEST PRODUCTS
Tubular Screw Conveyor
【Capacity】6-50 m3/h【Procesible Material】 …
Heavy Plate Feeder
Capacity: 100-240 m3/h Power: 15-45 kW Speed: 0…
Plate Magnetic Separator
【Capacity】8-35 t/h 【Power】1.5-3 kW 【Applic…