A specific tungsten, molybdenum, bismuth, and fluorite polymetallic deposit is a polymetallic deposit dominated by tungsten and bismuth, accompanied by molybdenum, tin, fluorite, and garnet.
Ore Properties
Chemical composition of ores
The chemical synthesis of the ore is shown in Table 1. The phase analysis results of the ore’s tungsten, molybdenum, bismuth, and iron are shown in Tables 2, 3, 4, and 5.
| Table 1: Analysis Results of Ore Chemical Composition (%) | ||||||||||||
| Element | WO3 | Mo | Bi | Sn | TFe | Mn | Pb | Zn | Cu | Be | S | P |
| Content | 0.55 | 0.083 | 0.18 | 0.073 | 6.82 | 0.64 | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.009 | 0.68 | 0.015 |
| Element | C | F | FeO | TiO2 | CaO | MgO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | K2O | Na2O | Au | Ag |
| Content | 0.78 | 8.02 | 3.62 | 0.10 | 21.92 | 0.76 | 43.31 | 9.34 | 1.58 | 0.74 | 0.06 g/t | 6.4 g/t |
| Table 2: Chemical Phase Analysis Results of Ore Tungsten (%) | |||||
| Tungsten Phase | Scheelite | Wolframite | Tungsten Hua | Silicate | Total Tungsten |
| WO3 Content | 0.38 | 0.17 | 0.008 | 0.003 | 0.561 |
| WO3 Distribution Rate | 67.74 | 30.30 | 1.43 | 0.53 | 100.0 |
| Table 3: Chemical Phase Analysis Results of Ore Molybdenum (%) | ||||
| Molybdenum Phase | Molybdenite | Scheelite | Molybdenum | Total Molybdenum |
| Molybdenum Content | 0.0753 | 0.0032 | 0.0045 | 0.062 |
| Molybdenum Distribution Rate | 90.72 | 3.86 | 5.42 | 100.0 |
| Table 4: Chemical Phase Analysis Results of Ore Bismuth (%) | ||||
| Bismuth Phase | Bismuthite | Natural Bismuth | Bismuth Oxide | Total Bismuth |
| Bismuth Content | 0.115 | 0.0282 | 0.0273 | 0.1705 |
| Bismuth Distribution Rate | 67.45 | 16.54 | 16.01 | 100.0 |
| Table 5: Chemical Phase Analysis Results of Ore Iron (%) | ||||
| Iron Phase | Iron Sulfide | Magnetic Iron | Silicates, etc. | Total Iron |
| Iron Content | 0.35 | 1.40 | 5.07 | 6.82 |
| Iron Distribution Rate | 5.13 | 20.53 | 74.34 | 100.0 |
It can be seen from Table 1 that tungsten, bismuth, and molybdenum are the main valuable elements in the ore, and iron and fluorine are associated useful elements. As can be seen from Tables 2 to 5, tungsten mainly exists in the form of scheelite and wolframite. The total distribution rate of black and white tungsten is 98.04%, and the ratio of black and white tungsten distribution rates is 1 2.3. Fluorine is mainly found in fluorite. Although the iron grade of the ore is low, only 6.82%, the phase analysis results show that about 20% of the iron exists in magnetite and can be recycled by the magnetic separation method.
Ore mineral composition
There are 73 minerals in the ore. Tungsten minerals include scheelite, wolframite, pseudo-semi-artificial scheelite, and tungsten minerals. Chromium minerals include molybdenite and molybdenite. Bismuth minerals include bismuthite, natural bismuthite, bismuthite, and orthorhombic bismuthite. Molybdenum minerals include molybdenite and molybdenite. Other metallic minerals include cassiterite, chalcopyrite, bornite, pyrite, magnetite, etc. Non-metallic minerals include garnet, fluorite, calcite, quartz, turtle amphibole, chlorite, and mica.
Main mineral particle size
The particle size distribution of the main minerals in the ore is shown in Table 6.
| Table 6: Main Mineral Particle Size Distribution (%) | |||||||
| Particle Size | Scheelite | Wolframite | Bismuthite | Molybdenite | Fluorite | Pyrite | Garnet |
| 0.417 | 4.14 | 5.28 | 2.75 | 23.53 | 41.47 | 40.31 | |
| -0.47+0.295 | 1.38 | 1.72 | 3.95 | 1.34 | 10.29 | 11.21 | 13.95 |
| -0.295+0.208 | 2.7 | 17.00 | 2.40 | 1.95 | 11.80 | 9.19 | 13.48 |
| -0.208+0.147 | 4.65 | 5.65 | 2.60 | 1.62 | 8.76 | 8.26 | 9.08 |
| -0.147+0.104 | 6.06 | 13.32 | 3.65 | 11.95 | 10.34 | 7.62 | 8.31 |
| -0.104+0.074 | 5.71 | 5.31 | 2.31 | 9.59 | 8.82 | 5.90 | 5.72 |
| -0.074+0.04 | 12.06 | 19.44 | 9.46 | 13.49 | 10.80 | 7.14 | 4.88 |
| -0.043+0.020 | 20.81 | 10.59 | 12.00 | 20.56 | 11.29 | 5.14 | 3.79 |
| -0.020+0.015 | 17.10 | 5.98 | 7.19 | 11.34 | 1.80 | 1.28 | 0.39 |
| -0.015+0.010 | 13.89 | 7.05 | 14.96 | 17.87 | 1.66 | 1.39 | 0.32 |
| -0.010 | 11.5 | 8.66 | 51.47 | 7.54 | 0.91 | 1.40 | 0.13 |
| The average particle size | 0.026 | 0.030 | 0.010 | 0.029 | 0.078 | 0.097 | 0.167 |
As can be seen from Table 6, the order of decreasing particle size of the main minerals is garnet > pyrite > fluorite > wolframite, scheelite, and molybdenite > bismuthite.
Mineral Processing Technology Progress
Application of complete flotation process
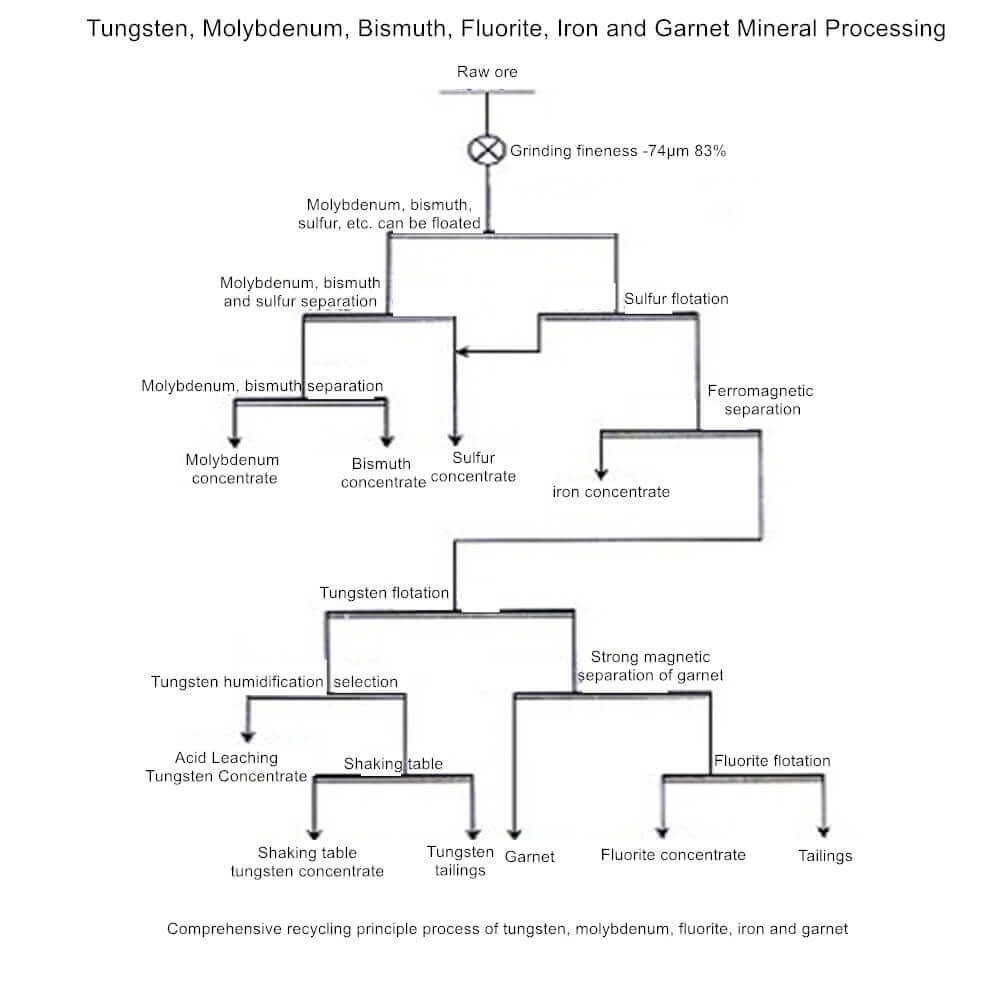
Because tungsten minerals are brittle and easy to muddy during the crushing and grinding processes, methods such as stage grinding, stage separation, coarse grinding and early harvest, gravity separation-flotation combined process, etc., are often used to recover coarse-grained tungsten minerals. To reasonably recover molybdenum, bismuth, tungsten, and fluorspar in the ore, the main process flows of total flotation, gravity separation-flotation, and flotation-gravity separation-flotation are proposed.
Full flotation process
The raw ore is ground once to the particle size (90%-74μm), where all valuable minerals are dissociated into monomers. The sulfide ore is floated first, then the tungsten mineral is floated, and finally, the fluorspar is floated. The advantage of this process is that the sulfide ore is recovered at one time, with only flotation operation, the slurry is transported smoothly, and the process flow is relatively simple. The disadvantage is that the raw ore is finely ground at one time to the particle size where the valuable mineral monomers are dissociated, and the tungsten mineral is easily muddied, which affects the improvement of the tungsten recovery rate.
Gravity-flotation process
The raw ore is ground to -0.5mm and is first subjected to gravity separation to obtain gravity separation rough sand. The tailings are then ground to a particle size where all useful minerals are monomer dissociated (90%-74μm), and then the sulfide ore, Tungsten minerals, and fluorite. After gravity separation and regrinding, the sulfide ore and scheelite are recovered by flotation sequence, and the tailings are recovered by shaking table to recover wolframite. Another gravity separation-flotation backbone process uses gravity separation (spiral chute) to process the settled sand in the grinding circuit to obtain gravity separation rough sand. The rest of the gravity separation-flotation backbone process is the same as the above gravity separation-flotation backbone process. The advantage of this process is that rough grinding and gravity separation can recover tungsten and prevent over-grinding of tungsten minerals, which is beneficial to the recovery of tungsten. The disadvantage is that some molybdenum sulfide and bismuth sulfide minerals also enter the gravity-selected rough sand with coarse-grained tungsten minerals. Therefore, there are two systems for the recovery of molybdenum, bismuth and tungsten. The process flow is relatively complicated, which brings inconvenience to production management.
Flotation-gravity-flotation process flow
Grind the ore to 60%-65%-74μm, first float the sulfide minerals of molybdenum and bismuth, and carry out gravity separation of the sulfide ore flotation tailings to obtain black and white tungsten mixed concentrate, and then grind the tailings to 90%-74μm. Sequential flotation recovers sulfide ores, tungsten minerals, and fluorspar. Similar to the gravity separation-flotation backbone process, the advantage of this process is that tungsten is recovered by coarse grinding and gravity separation, the degree of sludge of tungsten minerals is low, and the tungsten recovery rate is high. The disadvantage is that the gravity separation of rough sand and the sulfide ore flotation tailings require the recovery of molybdenum, bismuth, and tungsten, and the process flow is complicated.
| Table 7: Advantages and Disadvantages of 3 Processes | |||||
| Process Flow | The Degree of Mudification of Tungsten Minerals | Molybdenum, Bismuth & Sulfur Mineral Recovery System | Tungsten Mineral Recovery System | Process Complexity | Production Management |
| Full Flotation | Larger | 1 pcs | 1 pcs | Simpler | More convenient |
| Gravity Separation – Flotation | Small | 2 pcs | 2 pcs | More complex | Inconvenient |
| Flotation – Gravity Separation – Flotation | Small | 2 pcs | 2 pcs | More complex | Inconvenient |
Sulfide ore fully mixed flotation solution
Non-polar oil and sulfhydryl compounds are used as collectors to flotate all sulfide minerals from the raw ore. The tailings enter the tungsten flotation circuit, and lime is added to the sulfide ore mixed concentrate to suppress pyrite. The tailings are pyrite concentrate, the foam product is molybdenum-bismuth mixed concentrate, the foam product is molybdenum concentrate, flotation molybdenum minerals, the foam product is molybdenum concentrate, and the tailings are bismuth concentrate. A simple process flow characterizes the process. The disadvantage is that the natural floatability of minerals is not utilized, the separation of molybdenum and bismuth and the separation of bismuth and sulfur are difficult, and the quality of molybdenum concentrate and bismuth concentrate could be better.
Floatable solutions such as molybdenum and bismuth
Use non-polar oil as a collector to flotate all molybdenum minerals and most easily floatable bismuth minerals from the raw ore. The molybdenum-bismuth mixed concentrate is added with sodium sulfide to suppress the bismuth minerals, and the molybdenum minerals are flotated. The foam product is molybdenum concentrate, and the product in the tank is bismuth concentrate.
- Add mercapto-based collectors to floatable tailings such as molybdenum and bismuth to inhibit bismuth minerals and pyrite. Use lime or bleaching powder as inhibitors to separate bismuth and sulfur to obtain bismuth concentrate.
- The sulfur concentrate and bismuth-sulfur mixed flotation tailings enter the tungsten flotation circuit. This process fully uses the natural floatability difference of molybdenum and bismuth sulfide minerals. It is easier to separate the molybdenum and bismuth concentrate and the bismuth and sulfur mixed concentrate, and the molybdenum and bismuth mineral processing index is high. The disadvantage is that the number of process operations is large.
Molybdenum and sulfur mixed flotation scheme
Sodium sulfide is used to suppress bismuth minerals, molybdenite, and pyrite in the raw ore are mixed with non-polar oil flotation, and sodium sulfide is added to the molybdenum-bismuth mixed concentrate for molybdenum-sulfur analysis.
LATEST PRODUCTS
-
Tubular Screw Conveyor
【Capacity】6-50 m3/h 【Procesible Material】 …
-
Heavy Plate Feeder
Capacity: 100-240 m3/h Power: 15-45 kW Speed: 0…
-
Plate Magnetic Separator
【Capacity】8-35 t/h 【Power】1.5-3 kW 【Applic…