This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Home > Aggregates Processing Plant > Barite Aggregate Processing
Barite Crushing & Grinding Plant

Material: Barite
Application: It can be used not only as a white pigment but also in industrial sectors such as the chemical industry, paper making, textile filler, etc. It can act as a flux in glass production and increase the brightness of glass, etc., of which 80%-90% are used as Mud weighting agent in oil drilling.
Equipment: Jaw crusher, cone crusher, impact crusher, hammer crusher, sand making machine, vibrating feeder, vibrating screen, etc.
Barite Introduction
Barite or baryte is a naturally occurring mineral composed mainly of barium sulfate (BaSO4). Its name is originally derived from the Greek word “barys” meaning “heavy.” Barite has a high specific gravity, typically ranging from 4.0 to 4.6, making it one of the densest non-metallic minerals. The high specific gravity of barite makes it suitable for various industrial, medical, and manufacturing uses, particularly as a weighting agent in drilling fluids used in oil and gas exploration. Barite also serves as the principal ore of barium.
Barite’s Colors
Barite can occur in various colors, ranging from colorless to white and shades of blue, yellow, gray, and brown. The color of barite is influenced by impurities present in the mineral. Impurities and associated minerals in the same specimen can also influence the color of barite. In some cases, barite crystals may exhibit zoning or color variations within a single crystal, showcasing different colors or color intensities in different crystal parts.
Formation of Barite
Barite often occurs as concretions and void-filling crystals in sediments and sedimentary rocks. It is especially common as concretions and vein fillings in limestone and dolostone. Where these carbonate rock units have been heavily weathered, large accumulations of barite are sometimes found at the soil-bedrock contact. Many of the commercial barite mines produce from these residual deposits.
Barite is also found as a concretion in sand and sandstone. These concretions grow as barite crystallizes within the interstitial spaces between sand grains. Sometimes crystals of barite grow into interesting shapes within the sand. These structures are known as “barite roses”. They can be up to several inches in length and incorporate large numbers of sand grains. Occasionally barite is so abundant in a sandstone that it serves as the “cement” for the rock.
Barite is also a common mineral in hydrothermal veins and is a gangue mineral associated with sulfide ore veins. It is associated with antimony, cobalt, copper, lead, manganese, and silver. In a few locations, barite is deposited as a sinter at hot springs.
Barite Composition
Barium oxide (BaO): 65.7%
Sulfur trioxide (SO3): 34.3%
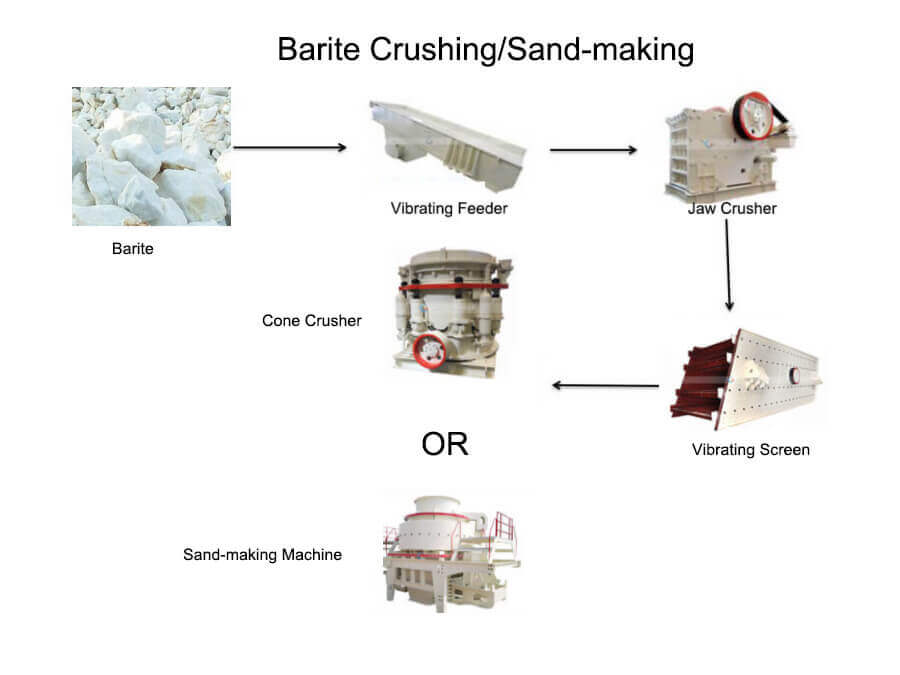
Barite Aggregate Processing
First, use the primary jaw crusher to crush barite. (The jaw crusher is used for coarse crushing of barite). And use the circular vibration screen to screen the material from the primary jaw crusher. Send the screened material for the secondary crushing(cone crusher or sand-making machine).
The barite sand-making machine has the functions of medium crushing, fine crushing, ultra-fine crushing, etc. It has a good crushing effect on hard materials, is intelligent and environmentally friendly, can be operated remotely, has a larger output, and has a complete range of finished stones. It is widely used in mining, metallurgy, building materials, water conservancy, and other industries.
Barite Grinding Plant
Crush barite sequentially using a primary jaw crusher and impact crusher (or fine jaw crusher). The jaw crusher is used for the coarse crushing of barite, and the impact crusher is used for the fine crushing of barite. After the barite material is finely crushed, screen it by circular vibration and deliver it to the ultrafine mill for grinding.
Barite Raymond mill is suitable for all non-metallic minerals, materials with Mohs hardness less than 7 and water content less than 6%. It can be widely used in diabase, coal gangue, wollastonite, graphite, clay, kaolin, Lime, zircon sand, bentonite, manganese ore, etc.
Barite Powder Making Plant
Barite powder making is generally divided into barite coarse powder processing (0-3MM), fine powder processing (20 mesh-400 mesh), barite ultra-fine powder deep processing (400 mesh-1250 mesh), and micro powder processing (1250 mesh – 3250 mesh).
Stage 1: Crushing
The barite bulk material is crushed by the crusher to the feed fineness (15mm-50mm) that can enter the mill.
Stage 2: Grinding
The crushed barite small pieces are sent to the silo by elevator and then evenly and quantitatively sent to the grinding chamber of the mill by the vibrating feeder for grinding.
Stage 3: Grading
The powder classifier classifies the ground materials, and the unqualified powder is classified by the classifier and returned to the main machine for re-grinding.
Stage 4: Collecting Powder
The powder meeting the fineness enters the dust collector with the airflow through the pipeline for separation and collection. The collected finished powder is sent to the finished product silo by the conveying device through the discharge port and then uniformly packed by a powder tanker or an automatic baler.
Barite Processing Solutions
Barite Processing Plant
10TPH Lead, Zinc, Barite & Various Sulfide Ores Flotation Process Plant