Metal is a substance with luster, good electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, mechanical properties, and a positive temperature coefficient of resistance. Metals are a big family, and 86 kinds of metals exist worldwide. Usually, people divide metals into ferrous and non-ferrous metals according to their color and properties. Today we mainly discuss ferrous metals and their beneficiation method.
What Are Ferrous Metals?
Ferrous metals mainly refer to iron and its alloys, such as steel, pig iron, iron alloys, cast iron, etc. They are known and used for their strength.

Application
- The properties they possess make them perfect to be used in industrial and architectural sectors for projects like skyscrapers, bridges, railroad projects, and vehicles.
- Due to their magnetic properties, ferrous metals are widely used in various appliances and engines. Ferrous metals, however, have high carbon content, which generally makes them more likely to rust; stainless steel is an exception due to its chromium content, as is wrought iron, due to the purity of its iron content.
- Ferrous metals are widely used in almost all industries, such as in manufacturing shipping containers, industrial piping, automobiles, railroad tracks, ships, and many commercial and domestic tools.
Which Metals Are Ferrous Metals?
Ferrous metals include iron, chromium, manganese, and their alloys, such as steel, pig iron, cast iron, ferroalloys, manganese, chromium, vanadium, titanium, etc. Iron, chromium, and manganese are not black. Pure iron is silver-white, chromium is gray-white, and manganese is silver-white.
- Steel
It is a general term for iron-carbon alloys with a carbon content between 0.02% and 2.11% by mass. The chemical composition of steel can vary greatly, and steel containing only carbon elements is called carbon steel (carbon steel) or ordinary steel. - Pig Iron
It is an iron-carbon alloy with more than 2% carbon content. The carbon content of industrial pig iron is generally 2.11%-4.3% and contains elements such as Si, Mn, S, and P. It is smelted from iron ore by a blast furnace. - Cast Iron
A general term for alloys is mainly iron, carbon, and silicon. In these alloys, the carbon content exceeds that which can retain in an austenitic solid solution at the eutectic temperature. - Ferroalloy
In a broad sense, ferroalloy refers to a product added to molten iron as a deoxidizer, element additive, etc., during steelmaking to make the steel have specific characteristics or meet particular requirements. - Manganese
A chemical element, element symbol Mn, atomic number 25, the simple substance is a gray-white, hard, brittle, shiny transition metal. Pure metal manganese is a metal slightly softer than iron, and manganese with a small number of impurities is hard and brittle and will oxidize in wet places. - Chromium
A chemical symbol Cr, atomic number 24, belongs to the VIB group in the periodic table of elements. The element’s name comes from the Greek word meaning “color” because chromium compounds have colors. The aspect is gray steel metal, the hardest metal in nature.
Ferrous Metals Beneficiation
Iron Process
There are many types of iron ore, and different iron ore processing technologies are also entirely different. The beneficiation process is to choose different beneficiation methods according to the properties of different ores to achieve the best beneficiation effect.
Common iron ore beneficiation technology
Magnetic separation of ore
Single magnetite ore: Most of the iron minerals in single magnetite ore are magnetite, which has the longest history of beneficiation and production. Due to the simple composition of the ore, the weak magnetic separation method is often used.
Polymetallic magnetite ore: Generally, the combined process of weak magnetic separation and flotation is adopted. Use weak magnetic separation to recover iron and flotation to recover sulfide or apatite.
Weak magnetic iron ore
Single weak magnetic iron ore: 1. Roasting magnetic separation 2. Gravity separation, flotation, strong magnetic separation, or its combined process.
Polymetallic weak magnetic iron ore: It uses gravity separation, flotation, strong magnetic separation or combined processes, and recovery of phosphorus or sulfide by flotation to process this kind of iron ore.
Magnet-Red (Ring) Iron Ore
Single magnet – red (rhombus) iron ore: 1. Weak magnetic separation combined with gravity separation, flotation, and strong magnetic separation. 2. Magnetic roasting magnetic separation method or parallel process with other methods.
Containing polymetallic magnet-red (magnetite) iron ore: the beneficiation method of this type of ore is the most complicated in iron ore, and a combined process of weak magnetic and other methods is generally adopted, that is, use weak magnetic separation to recover magnetite; Weak magnetic iron minerals are recovered by gravity separation, flotation or strong magnetic separation and associated components are recovered by flotation.
Chromium Process
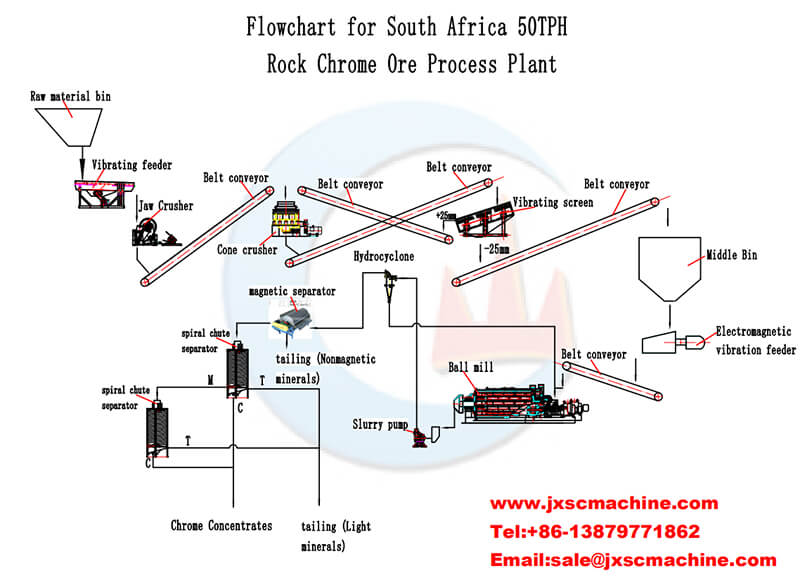
The chrome ore beneficiation process mainly adopts the gravity separation method. The leading equipment is the jig, shaking table, spiral separator, centrifugal concentrator, spiral chute, etc. Sometimes the gravity concentrate will be re-selected by weak or magnetic solid separation to improve further the grade of chromium concentrate and the ratio of chromium to iron. In addition, some mines will also use methods such as flotation and flocculation flotation. For chromium ore beneficiation, according to the ore analysis report and the beneficiation test report, choose the final beneficiation method.
Manganese Process
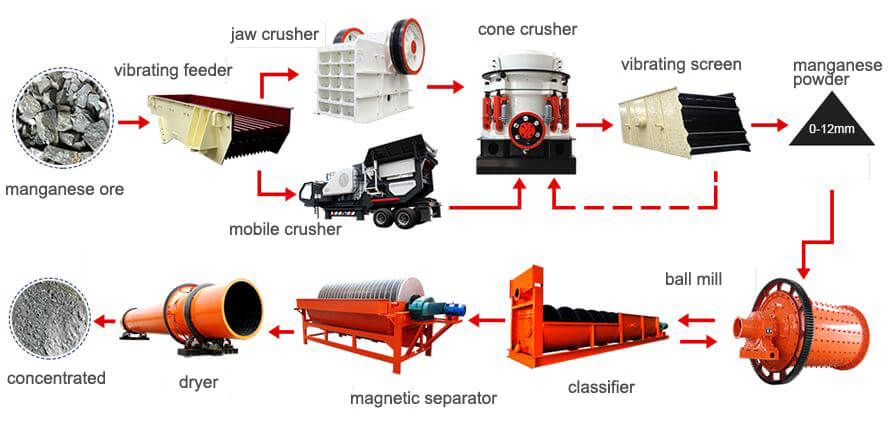
Because most manganese ores are fine-grained or fine-grained inlaid, and there are a considerable amount of high phosphate ore, high iron ore, and common (associated) valuable metals, it brings great difficulty to the separation. The common manganese beneficiation methods include:
- Physical beneficiation – Washing and screening method, gravity separation method, strong magnetic separation method, flotation method, the combined beneficiation method
- Chemical beneficiation – Leaching method
- Special beneficiation – Fire enrichment method
In actual production, the manganese beneficiation methods are as:
Manganese carbonate ore primarily uses strong magnetic separation, heavy medium beneficiation, and flotation. Manganese oxide ore is mainly based on gravity separation, primarily using the washing-gravity separation process or ore washing-reduction roasting magnetic separation-gravity separation process. Of course, for refractory manganese ore, combining two or even multiple beneficiation methods for separation is often necessary.
LATEST PRODUCTS
Twin Screw Feeder
【Feeding Capacity】 10-160 t/h【Power】 2.2-…
Tubular Screw Conveyor
【Capacity】6-50 m3/h【Procesible Material】 …
Heavy Plate Feeder
Capacity: 100-240 m3/h Power: 15-45 kW Speed: 0…