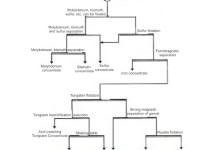
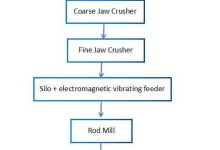
Multi-metal Beneficiation Process for Tungsten, Bismuth & Molybdenum
A specific tungsten, molybdenum, bismuth, and fluorite polymetallic deposit is a polymetallic deposit dominated by tungsten and bismuth, accompanied by molybdenum, tin, fluorite, and garnet. Ore Properties Chemical composition of ores The chemical synthesis of the ore is shown in Table 1. The phase analysis results of the ore’s tungsten, molybdenum, bismuth, and iron … Continue reading Multi-metal Beneficiation Process for Tungsten, Bismuth & Molybdenum