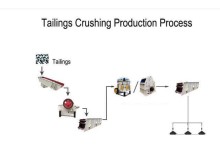
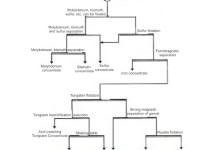
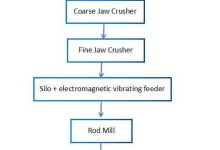
Quartz
Quartz is one of the most common minerals in the Earth’s crust. As a mineral name, quartz refers to a specific chemical compound (silicon dioxide, or silica, SiO2), having a specific crystalline form (hexagonal). It is found is all forms of rock: igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary.